What is a LoRaWAN Gateway?
By Kezang Loday 1 year agoLoRaWAN is a key technology in the IoT landscape, connecting battery-operated devices to the internet across various networks. This blog focuses on LoRaWAN Gateways, the vital link between end devices and the network server. This blog explores the fundamental aspects of LoRaWAN Gateways, it’s functionality, importance, benefits, and the wide range of IoT applications they support, including smart cities, agriculture, asset tracking, and environmental monitoring.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a transformative technology that is redefining how we live and work.One of the key technologies enabling IoT is LoRaWAN which stands for Long Range Wide Area Network. LoRaWAN is a low-power wide-area network (LPWAN) protocol that connects battery-operated devices to the internet in regional, national, or global networks. It is based on LoRa, a modulation technique that uses chirp spread spectrum (CSS) technology developed by Semtech Corporation.
Usually, a LoRaWAN network operates in a 4 layer architecture as follow(you can explore more details about how LoRaWAN and other LPWAN technologies work, you can refer to our previous blog here):
- End Nodes: These are the edge devices or sensors capturing data.
- Gateway: This component gathers data from multiple end nodes.
- Network Server: It aggregates data from the gateways to send to the application server.
- Application Server: This server processes and possibly visualizes the aggregated data.
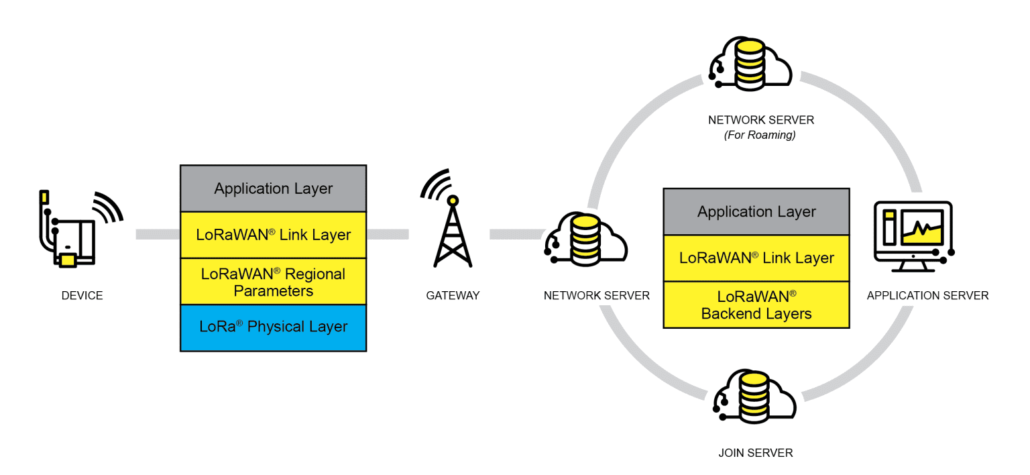
LoRaWAN Network Architecture, Credit: LoRa Alliance
In the architecture, the LoRaWAN gateway plays a pivotal role in the LoRaWAN network architecture by facilitating bidirectional communication between end-user nodes and forwarding data to the LoRaWAN servers, enabling seamless connectivity and efficient data transmission within the network. To better understand LoRaWAN Gateway for your IoT projects, I invite you to explore thoroughly about LoRaWAN Gateway in this blog which includes:
What is a LoRaWAN Gateway?
A LoRaWAN Gateway is a crucial component of the LoRaWAN network architecture. It acts as a bridge between end devices (such as our SenseCAP sensors) and the network server.
A LoRaWAN gateway has a LoRa concentrator, which allows it to receive radio signals sent by LoRaWAN devices, and convert them to a format compatible with a server, such as Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and even Cellular 3G/4G, to send data to the cloud. It collects or concentrates data from several end nodes and forwards it to the network server. It is much like a Wi-Fi router but designed for IoT devices.
A Gateway can support thousands of end nodes within its coverage area, which can range from a few kilometers to tens of kilometers, depending on the environment and the antenna. It does not perform any data processing or filtering, but simply acts as a transparent bridge.
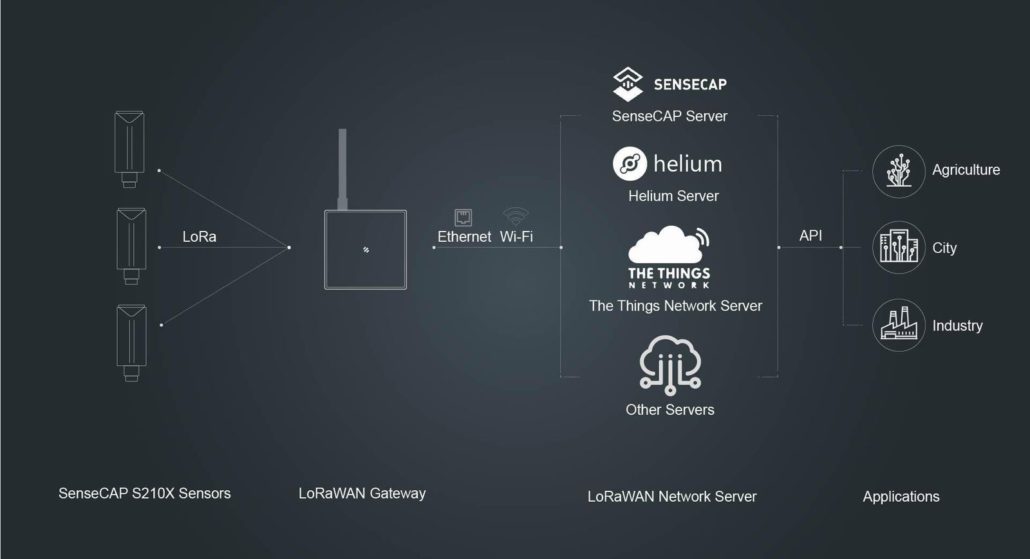
How a LoRaWAN Gateway Works?
A LoRaWAN Gateway operates on a star-of-stars topology, where multiple end nodes communicate with one or more gateways, and the gateways communicate with a single network server. The communication between the end nodes and the gateways is bidirectional, meaning that the end nodes can send uplink messages to the gateways, and the gateways can send downlink messages to the end nodes. However, the communication between the gateways and the network server is unidirectional, meaning that the gateways can only send uplink messages to the network server, and the network server can only send downlink messages to the gateways.
The gateway ensures that data packets from the end nodes are forwarded to the network server in a timely and efficient manner, and it also manages the transmission of commands from the network server to the end nodes. This helps to ensure that the LoRaWAN network operates smoothly and efficiently, even when dealing with large amounts of data from many end nodes.
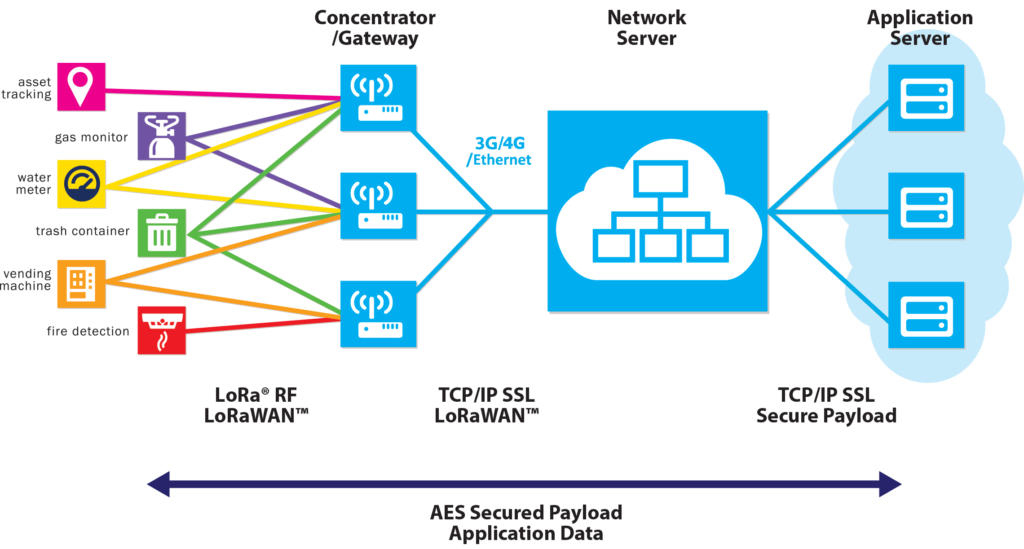
Credit: The Things Network
Why do we need a LoRaWAN Gateway?
A LoRaWAN Gateway is essential for enabling LoRaWAN connectivity for IoT devices. Without a LoRaWAN Gateway, the end nodes would not be able to communicate with the network server and the application server, and thus would not be able to access the Internet or other cloud services. A LoRaWAN Gateway acts as a bridge between the LoRaWAN network and the Internet, allowing data to be transferred between the physical and the digital worlds. Therefore, LoRaWAN is the backbone of the LoRaWAN IOT architecture and the LoRaWAN IOT Network wouldn’t exist without it.
Benefits of using LoRaWAN Gateways
Using LoRaWAN Gateways for IoT applications can bring several benefits, such as:
Long-range communication: LoRaWAN Gateways can provide wireless connectivity for end nodes over long distances, 2 kilometers in urban areas and up to 15 kilometers in rural aread, depending on the environment and the antenna. This is ideal for applications that require wide-area coverage, such as smart city, smart agriculture, and asset tracking.
Low-power consumption: It can enable low-power communication for end nodes, as LoRa modulation is designed to minimize the power consumption and maximize the battery life. This is ideal for applications that require long-term operation, such as environmental monitoring, smart metering, and wildlife tracking.
High scalability: It can support high scalability for end nodes, as LoRaWAN network can accommodate millions of devices with minimal infrastructure and interference. This is ideal for applications that require massive deployment, such as smart lighting, smart parking, and smart waste management.
Robust security: It can ensure robust security for end nodes, as LoRaWAN network uses end-to-end encryption, authentication, and integrity protection. This is ideal for applications that require sensitive data transmission, such as healthcare, industrial control, and smart home.
Applications of LoRaWAN Gateways
LoRaWAN Gateways has a wide range of applications, few of them are:
Smart City: LoRaWAN Gateways can provide connectivity for smart city applications, such as traffic management, air quality monitoring, waste management, parking management, and public safety. LoRaWAN Gateways can help improve the urban efficiency, sustainability, and livability.
Smart Agriculture: LoRaWAN Gateways can provide connectivity for smart agriculture applications, such as soil moisture monitoring, crop health monitoring, livestock tracking, irrigation control, and pest detection. LoRaWAN Gateways can help optimize the agricultural productivity, profitability, and quality.
Asset Tracking: LoRaWAN Gateways can provide connectivity for asset tracking applications, such as vehicle tracking, container tracking, luggage tracking, and bicycle tracking. LoRaWAN Gateways can help locate and manage the assets in real-time, reducing the risk of loss, theft, or damage.
Environmental Monitoring: LoRaWAN Gateways can provide connectivity for environmental monitoring applications, such as weather monitoring, water quality monitoring, wildfire detection, and earthquake detection. LoRaWAN Gateways can help collect and analyze the environmental data, enabling early warning and mitigation of natural disasters.
Credit: Wyld Networks
LoRaWAN Gateway Products Recommendation
Choosing the right hardware is crucial for the success of building your LoRaWAN network. Seeed Studio offers robust and reliable LoRaWAN Gateways, offering a blend of performance and user-friendly features. It supports a multitude of end nodes, ensuring efficient data transmission and network longevity.
The following 3 are ready-to-deploy LoRaWAN gateway devices, which you can deploy to set up the network directly after getting them:

However, if you’re a developer who prefers to build your own LoRaWAN gateway from scratch, we got you covered too. With the following gateway modules, Raspberry Pi Hat, dev kit, and the tutorial here, you can build your very own gateway with a Raspberry Pi.


WM1302 Raspberry Pi Hat to develop your LoRa gateway with Raspberry Pi
References
What is the internet of things? | IBM
What is LoRaWAN® Specification – LoRa Alliance® (lora-alliance.org)
What’s A LoRaWAN Gateway And Why Do You Need One? – Artificial Intelligence + (aiplusinfo.com)
What is a LoRaWAN Gateway? (wyldnetworks.com)
A Gentle Introduction to LoRaWAN Gateways & Nodes – Latest Open Tech From Seeed (seeedstudio.com)
LoRaWAN Gateway, Module, Applications & Protocol – IoT Made Easy (rakwireless.com)


