Top 10 Greenhouse Gardening Mistakes: How to Solve them by Using Soil Sensors and Air Sensors
Greenhouses are a perfect fit for some professional gardeners or some planting enthusiasts to grow some plants in the garden. Growing plants is no easy task, however, and the actual practice of growing plants in a greenhouse requires a bit of balance and skills. In this blog, let’s discuss the top 10 Greenhouse Gardening Mistakes and how to solve them by using different sensors.

Didn’t Control the Temperature
One of the biggest mistakes gardeners make is forgetting to monitor the greenhouse temperature every day. Usually, in the hot season, the temperature of the Greenhouse might be more than 50 °C, but the cooling system might keep the Greenhouse temperature at a suitable range of 15~30 °C which will not impact the plant growth too much. In severe winter, the temperature of the Greenhouse should be 2-3 °C higher than the optimum temperature limit for the plant, because the soil temperature at a depth of 5 cm in the daytime can be 5-7°C lower than the indoor air temperature, and 3-5°C higher than the indoor air temperature at night, and the temperature range is between 13-26°C.
How to solve it?
The best way to control temperature is through ventilation, shade cloth, and heating. In some small Greenhouses, it will heat up very quickly in the summer. It’s better to open the ventilation windows in summer to cool down the small Greenhouse. Use a basic hanging thermometer or directly choose a smart greenhouse temperature and humidity sensor that can help you monitor real-time data and record the historical data for you to prevent plant or vegetable cost damage.

Didn’t Provide Enough Light
Light is an important element in the photosynthesis process. Sometimes it is necessary to control the light inside the Greenhouse, and light is an essential condition for vegetable growth. Without light, vegetables cannot produce chlorophyll and cannot grow properly. Therefore, when using greenhouses to cultivate vegetables, it is necessary to control the light. The light intensity varies greatly in different seasons.
Normally, there is less sunlight in winter and spring. Because the greenhouse is isolated from the light, the vegetables can receive very little light. During this period, farmers can lift the shed film or use incandescent lamps to ensure that the vegetables receive sufficient light.
You can choose a smart light intensity sensor to help you monitor the exact light intensity and provide optimal light conditions.

Didn’t Control Humidity
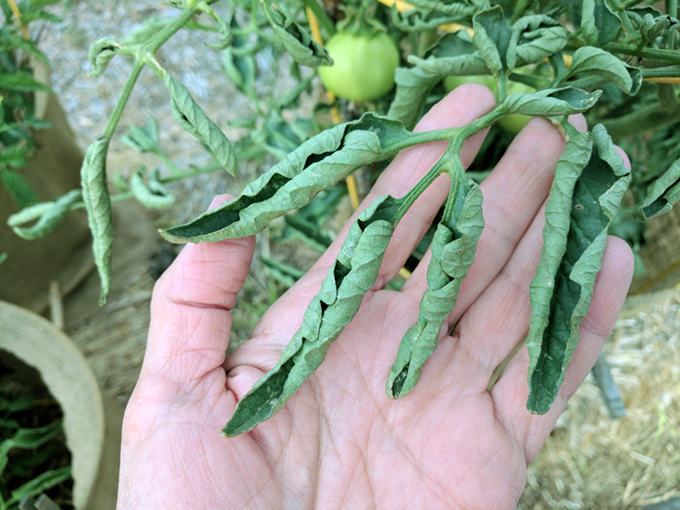
Humidity is a natural part of the Greenhouse cycle, as the plant grows, the plant absorbs water through the roots and evaporates it around the air. But the air can only absorb a limited amount of water, and that ability is decreased as the temperature drops. If the temperature changes rapidly, the plants will take serious damage plants, especially plants such as tomatoes and cucumbers, which are common greenhouse foods. And the humidity in the Greenhouse is too high, which may cause the plants to fail to grow or even die. Later I will explain what harm will happen if the humidity is not controlled. If you can’t confirm the current humidity in Greenhouse, you can buy a sensor to help you check the humidity.
Open the vent window in summer or when it’s hot so he doesn’t experience temperature spikes, and make sure to close the vents, etc at night to prevent overcooling. In winter, consider using a low-tech radiator like a bucket to stabilize the temperature. If you buy a humidity sensor, you will be able to see the humidity when dew is forming on the leaves of your plants, which is something you want to avoid. Like I said before, it is recommended to buy a multi-function sensor to monitor your plants. And we have a sensor that multi-function sensor with Temperature, Humidity, Soil sensor, and EC

Fungal Growth
As mentioned earlier, if the humidity in the greenhouse is not controlled, it will growth of mold and fungus. A warm and humid environment is an ideal place for many molds and fungi to grow. If the relative humidity in the greenhouse is high (over 85%), there is little air circulation, and there is water or dew on the leaves, mold can grow.
Air circulation is the key to preventing this, keeping it ventilated or using a fan is a good idea, and adequate spacing between plants is also very important. Using drip irrigation is another key preventative step in keeping leaves dry.
Common fungi in greenhouses include Botrytis, powdery mildew, and Botrytis nigra, with symptoms of spots, blight, rot, and other plant reactions. Sometimes you can’t see mold on the surface because the fungus is in the soil. You can use vinegar or bleach annually in your tools and greenhouses and use a smart soil sensor that helps you monitor soil conditions whether it is too wet or not.

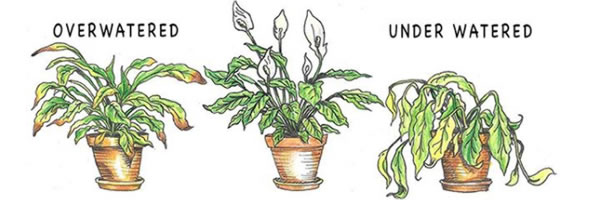
Over- or Under-watering
Drip irrigation is usually best for greenhouses. However, the number of drip irrigation should not be too much, it depends on the current humidity of the greenhouse. If the humidity of the greenhouse is not controlled, it is easy to dry out the greenhouse plants or overwater.
Every plant needs different watering times, you can water it in the morning and see how dry the plant is at the end of the day. This gives the plants time to transpire before the temperature rises. At the same time, you don’t want to give them too much water. If the weather is cloudy, the plant will absorb a lot of water, and if you keep watering it will make the soil too wet. It’s best to check them again later in the day for another watering.
You will have to water more often in the spring and summer when the plants are young and growing rapidly and the temperature is warmer. Sometimes the surface of the soil is dry or even cracked, but the deep soil is still moist. You can’t judge whether the deep soil is wet from the surface. Combined with the mistakes mentioned before, it is actually possible to have a product with temperature, humidity, and soil moisture sensor. With the current technological capabilities, a smart sensor has been manufactured with multiple functions including EC functions. Maybe you don’t know what benefits EC functions can bring to your Plants. I will explain later.
Deplete the Soil
Because you are often planting plants in the same place, the soil will become firm and lose its fertility and attract pests.
When you’re ready to make your bed, consider using a mixed soil mix in addition to your regular additions of compost and manure. But not replanting in pots that already have pests, in fact, many professional organic growers recommend using a soilless mix to prevent these problems.
These mixtures contain peat, coconut fiber, perlite, vermiculite, worm castings, and sometimes compost. However, since you need to keep buying these materials, for the hobbyist, just using really good quality compost can have the same benefits: maintaining a proper moisture balance and preventing fungus when you’re not sure your soil is healthy enough of course for now, right now there’s a smart sensor can identify your soil health through EC function. Soil EC that is too high or too low can hinder the growth of crops. That smart sensor will help you monitor all the mistakes mentioned earlier. If you want to know what an EC sensor is and how it works, you can read this blog.

No Ventilation
A greenhouse is an almost completely enclosed space. In this environment, plants may produce some toxic gases. If these gases are not discharged in time, the vegetables might not able to grow. At this point, you can get an air multi-function sensor that helps you track the air quality. However, when you open the windows, it does not mean that the greenhouse is being ventilated. – Air needs to flow through.
Since the hot air rises, this means pushing the hot air at the top out. You can draw cool air through the bottom and use the roof vents to let warm air escape. Sometimes a small fan is needed to keep the air moving.
Excessive Lighting / Sunlight
In the previous, we mentioned that there are times when you need to give your plants some light, but sometimes you might give your plants too much light without even noticing. Normally sunlight is best, but considering the summer exposure, the Greenhouse needs some mulch. Greenhouse covers have light transmittance. Standard plastic covers are 6mm and are durable, typically 91% light transmittance per layer. However, as the plastic ages and turns yellow, this transfer rate decreases. You may don’t know when‘s the time to change your plastic case by the plastic ages and turns yellow, So, you will not sure much light get lost in the transmits. You can use a sensor with a Light Intensity function to observe the current light transmittance of the greenhouse. This can remind you when it’s time to replace your plastic case

Plant the Wrong Plants Inside
At first, you think Greenhouse can grow all the plants you want, but they are also seasonal, and warmth is not good for everything. Experimentation is fun, but proper garden planning can turn you into a pro.
Know the comfortable temperature for the plants you want and maximize your garden space by using it to extend the season. This means planting vegetables in the winter, then using your greenhouse to start raising seedlings as the temperature warms up. When the weather is really warm, you can transplant tomatoes and other heat-loving crops. Stay focused for real results.
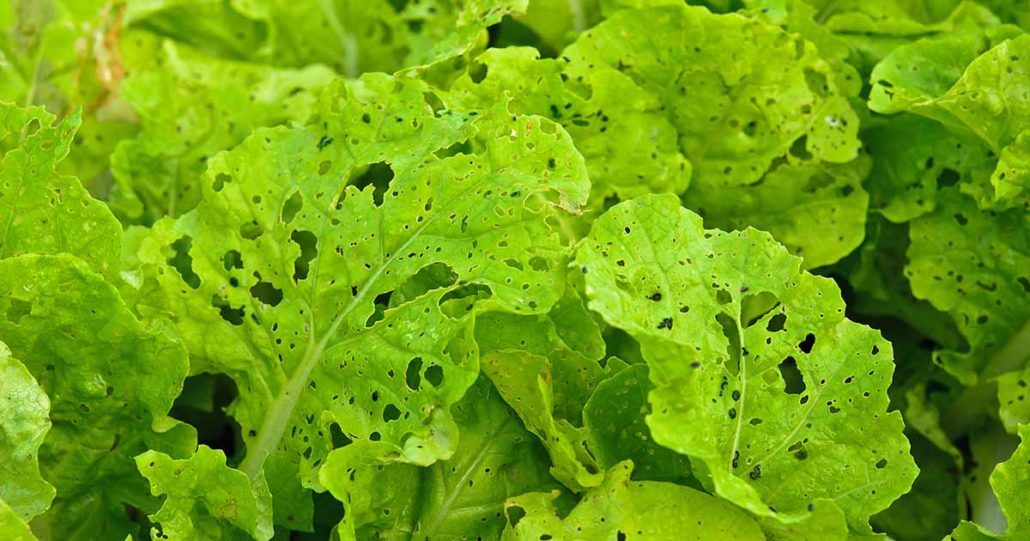
Ignore Pests
Prepare for the prevention of pests, Plants or vegetables will be damaged by pests and diseases at one or several stages, resulting in reduced yields. Farmers who grow vegetables should observe in time to prevent the occurrence of pests and diseases, take measures to eliminate pests and diseases to minimize the impact of pests and diseases, and do the cleaning for the greenhouse are important.
