What is Industry 4.0? – Technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Industry 4.0, or the fourth industrial revolution, is the latest and hottest trend in industrial transformation today. Encompassing key elements like cloud computing and big data, Industry 4.0 is bringing improvements to the way industries perform at scale! Don’t miss out on this exciting trend and join us today to learn about Industry 4.0 and its technologies!
This article will cover:
- Introduction to Industry 4.0
- Benefits of Industry 4.0
- Challenges Faced by Industry 4.0
- Industry 4.0: IIoT Case Studies
- The Future of Industry 4.0

What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 (I4.0) represents the fourth industrial revolution, but more specifically refers to the currently ongoing digital transformation in industries. Unique from its preceding industrial revolutions, I4.0 focuses on an information driven interconnectivity between people, devices, and systems, which is used to enable enhanced decision making in industrial processes.
The technologies encompassed by Industry 4.0 are often summarised as the constituent elements of a “Smart Factory”.
Imagine this:
In the factory of the future, no workers are required to be on the shop floor, as they can interact with all factory elements remotely and in real time with Augmented Reality. In the virtual space, they can perform a Simulation of operational decisions, which can be executed remotely through hydraulic arms – thanks to advanced Robotics.
While this happens, devices armed with sensors and wireless connectivity are scattered throughout the factory, connected in an Internet of Things (IoT), are working quietly in the background to send data to the cloud. This data can then be processed in real time with Edge Computing or on a far larger scale, ie. Big Data, Analytics & Artificial Intelligence with Cloud Computing!
What’s more, these are only a fraction of the possibilities enabled by Industry 4.0!
While some may perceive Industry 4.0 to be a framework or group of technologies, it may be more accurate to understand it as a more abstract paradigm of digital interconnectivity and smart, autonomous decision making. As new technologies emerge in the coming decade, they too will be a part of the fourth industrial revolution!
Benefits of Industry 4.0
While Industry 4.0 comprises numerous individual components, they are all targeted at bringing a unified set of benefits to transform how industries are working today, centred around productivity, flexibility, quality and speed.
Improved Productivity & Quality
You may have heard the phrase, “Data is the new gold!” – and it’s true! Data allows businesses to make better decisions backed by information from the real world. With the interconnectivity brought about by Industry 4.0, big data analytics such as machine learning becomes possible on an even larger scale.
Data allows us to identify areas for optimisation in supply chains, utilise resources better, and to impose tighter quality controls through extensive and widespread real time monitoring. On the other hand, businesses may also use data to drive core development decisions, such as whether to expand or diversify.
Knowledge Sharing & Collaboration
The prevalence of consistent data across multiple fields will also allow for intra-industry collaboration across multiple fields and dimensions. For example, Industry 4.0 allows data to be shared across production lines and business processors, allowing various sensor data to be instantly shared throughout the network. This data can then be utilised to instantaneously and autonomously bring improvements across multiple production lines, ie. machine-to-machine or system-to-system communication.
Potential for Innovation
Industry 4.0 serves to give a holistic view of industrial processes. Greater and deeper knowledge of manufacturing processes, supply & distribution chains and business performance represent opportunities to innovate. This may involve changing the business model, developing a new product, or implementing a new technology.
Safer Working Environments
As more dangerous tasks are automated or remotely operated, workers can enjoy greater occupational safety. With IoT devices and sensors, it’s also easier and more affordable than ever for businesses to implement smart safety measures. For example, many logistics companies are now exploring IoT devices that can monitor the condition of vehicle operators, allowing supervisors to ensure that they are healthy and sufficiently rested for the journey and reducing on-road risks.
Challenges Faced by Industry 4.0
Despite the benefits of Industry 4.0 that we have experienced so far, its full vision remains far from realised. This owes to several factors that increase the barriers to entry for companies exploring I4.0 initiatives.
1. Managerial Dissonance
While some parties may recognise the benefits of Industry 4.0, a digital transformation can be difficult to realise without close cooperation between different units. Some decision makers may also prefer to avert the risks associated with radical digitalisation.
2. Cybersecurity Concerns
Cybersecurity threats, such as from hackers, can be a significant deterrent to businesses that work with sensitive data. Furthermore, private infrastructure can be costly while trust concerns arise with third-party providers.
3. Lack of Expertise
Many technologies used in Industry 4.0 are new and require specific expertise to develop and operate. Businesses who do not have sufficient in-house expertise may struggle to effectively explore and implement them.
4. Dependence on Existing Infrastructure
Transforming existing business practices onto a new platform with new technologies is both monetarily and time consuming. This is even more so if current practices do not involve digital documentation or processes.
Because of these difficulties, the global industry has mostly partially adopted Industry 4.0 by implementing edge devices for monitoring and control systems. Nonetheless, the rewards from a comprehensive I4.0 digital transformation has been substantiated by global industry leaders like Amazon. Thus, the realisation of Industry 4.0 is not a matter of if, but when!
Industry 4.0 Case Studies
At Seeed, we specialise in delivering high-quality industrial IoT solutions to help you improve your processes, regardless of industry. In this section, I will share several examples of the IoT solutions developed with Seeed! These examples can also be found in our Industrial IoT article, where you can also read about IIoT in detail.
Industry 4.0 in Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the largest industry from an IoT spending perspective, bringing transformations to manufacturing operations, production asset management & maintenance, as well as field services. Apart from allowing the performance of manufacturing operations to be monitored efficiently, industrial IIoT in manufacturing can also be used to deliver services remotely and autonomously.
Odyssey x86J4105 in Field Service Manufacturing IIoT
At Seeed, we have helped our client build their smart juice machine based on the ODYSSEY X86J4105. The ODYSSEY is a powerful single board computer (SBC) with rich communication interfaces, which makes it an ideal candidate for edge computing in many applications.
The smart vending machine will automatically make freshly squeezed juice for the customer upon order, and is a fine example of field manufacturing enabled by industrial IoT. The machine possesses its own computing core to control the user interfaces and manufacturing actuators, which is also connected to the cloud for easy monitoring and maintenance.
Industry 4.0 in Agriculture
Unsurprisingly, agriculture is another industry that is transforming rapidly with Industry 4.0. Farming has always been at the forefront of scientific innovation – evolving from the handheld tools used centuries ago to farming machinery like tractors and bale harvesters and even genetically modified organisms.
What you may not know is that the optimisation agricultural production requires the careful monitoring and control of numerous environmental conditions, such as temperature, light levels, atmospheric composition, water usage, etc. In view of this, Industry 4.0 and specifically Industrial IoT offers the perfect solution for managing the required complex real-time data.
BeagleBone® Green in Agricultural IIoT
Seeed has had the privilege of implementing an Industrial IoT electronic controller for our customer’s Poultry Industry and Farm with the BeagleBone® Green. BeagleBone® Green is a collaborative effort between BeagleBoard.org and Seeed, based on the open-source design of BeagleBone Black. It sports two Grove connectors for easily deploying with sensor modules and ethernet internet connectivity.
The solution provides interconnectivity between agricultural systems and the cloud, allowing for real time remote monitoring of data. With more dense and precise measurements of environmental conditions, farming techniques and conditions can also be gradually optimised over time to improve productivity!
Industry 4.0 in Logistics & Transport
As part of Industry 4.0, Industrial IoT is commonly applied to transport fleet management and real time monitoring of logistics.
Fleet management involves the monitoring of vehicle movement and driver’s behaviour, and enables numerous smart functions such as automatic scheduling of transport movement with optimised routes and alerts for preventative maintenance. This improves safety by reducing the time spent on roads and flagging dangerous road behaviour, while saving fuel and repair costs.
On the other hand, sensors fitted onto vehicles can monitor the environmental conditions for transporting high value items such as fresh produce. By maintaining certain temperature, humidity, and pressure conditions, the condition of agricultural produce post transport can be drastically improved, better retaining their value and reducing manufacturer costs.
Logistics IIoT Monitoring with BeagleBone® Green
In fact, this was exactly what we implemented for one of our customers here at Seeed. By customising BeagleBone® Green to add power over ethernet (PoE) functionality and more I/O interfaces, we built a custom IIoT solution for collecting temperature and humidity data during fresh produce transport for quality tracking.
The data is uploaded to the cloud for monitoring and analysis, and can identify gaps in transport procedures. In all, this application of Industrial IoT in logistics prevents unnecessary costs and increases overall efficiency in product distribution, once again showing the potential of Industry 4.0.
Industry 4.0 is Still Transforming!
The fourth industrial revolution is an ongoing process. As new technologies and practices are researched and experimented with as we speak, there’s no telling what the future will hold for Industry 4.0! Nonetheless, here are a few of the latest updates and examples stemming from Industry 4.0.
Innovative Industrial Solutions
Numerous prototypes are currently being developed to take advantage of the new Industry 4.0 paradigm of data-driven interconnectivity.
Automated Thread Changer for Braiding Machines
This solution developed by ARK Industrie AG is an automatic thread changer that is remote controllable. Encompassing the defining elements of Industry 4.0, it was designed with preventive and corrective maintenance alerts and integrated material usage optimisation. It also features self-management: A smart solution that calculates the most effective production strategy for a given list of customer orders!
Automated Feeding System for Industrial Sewing Machines
This is another prototype from ARK, which is a mechatronic solution for automatic sewing in the textile industry. It is a collaborative robot that can be remotely monitored, which is also equipped with quality assurance measures through computer vision (machine learning).
TinyML: Machine Learning on the Edge
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have been the talk of the town for the past decade, and these applications are becoming a crucial part of Industry 4.0. Enabled by edge computing, Edge AI (or Edge Artificial Intelligence) is fitting AI applications into smaller and less powerful single board computers. But in reality, recent developments have shown that it’s not a farfetch to run ML even on microcontrollers that have only kilobytes of RAM!
TinyML, short for Tiny Machine Learning, is a subset of machine learning that employs optimisation techniques to reduce the computational space and power required by machine learning models. Specifically, it aims to bring ML applications to compact, power-efficient, and most importantly affordable microcontroller units.
Further fuelling the TinyML movement, companies like Edge Impulse & OpenMV are helping to make Edge AI more accessible through user-friendly platforms. Now, industries can easily deploy smart applications as part of their I4.0 digital transformation, even without prior expertise!
Read more about Edge AI and machine learning in our previous article.
Worldwide Connectivity with LR & LoRaWAN
LR & LoRaWAN are undeniably among the most relevant technologies in IoT and the movement towards Industry 4.0.
LR is a license-free sub-gigahertz radio frequency technology that enables long-range transmissions (up to 10km rural, 2km urban) while maintaining low power consumption. On the other hand, LoRaWAN is a protocol stack operating on LR that defines the network that connects LR -enabled devices and enables them to transmit data with cloud servers.
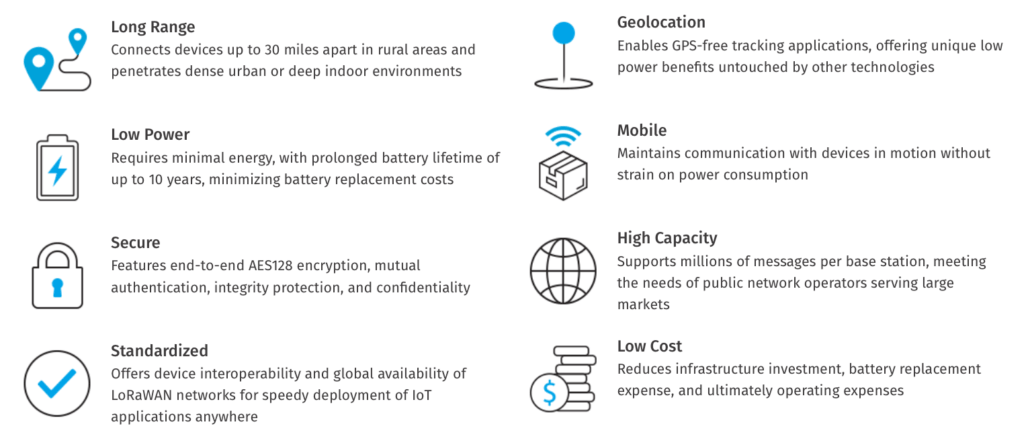
Together, LR & LoRaWAN are democratising the IoT space by bringing powerful and convenient wireless communication to industrial and infrastructural applications. We have seen them in agricultural monitoring, development of smart cities, and even home IoT.
To learn more about enabling Industry 4.0 IoT with LR & LoRaWAN, be sure to check out our detailed article on their applications!
Conclusion
In summary, Industry 4.0 represents a paradigm of data-driven interconnectivity between people, machines, and processes that has the potential to improve not only manufacturing, but also design, businesses and customer relationships. While a full realisation of the I4.0 vision is still a ways off, we can already begin reaping its advantages through partial adoption such as affordable IoT devices and networks!
Seeed offers industrial-grade services and products to aid your transformation in Industry 4.0 and IoT. To learn more, be sure to visit our Industrial Solutions and Online Store!
In addition, the following material may be of interest to you:
- What is Industrial IoT? [Case Studies]
- Edge AI – What is it and What can it do for Edge IoT?
- Cluster Computing on the Edge – What, Why & How to Get Started
- LR & LoRaWAN: Vertical Solutions for the Real World