Human Machine Interfaces in the Internet of Things (IoT)
Human Machine Interfaces or HMIs are devices that allow humans to interact with machine systems, but how much do you know about their various benefits and latest trends? Furthermore, HMIs are becoming an increasingly important aspect of various systems with the rise of IoT! Don’t miss out and join us in this article to find out all about Human Machine Interfaces in the Internet of Things!
We will be covering the following and more!
- What is a HMI?
- HMI vs PLC vs SCADA
- Benefits & Importance of HMIs
- HMI Trends & Developments
- Choosing a HMI
What is a HMI?
HMI stands for Human Machine Interface, and as its name suggests, it is a feature or component of a device or system that allows us to interact with it. HMIs are all around us – touchscreens keyboards are all examples of HMIs!
In an industrial setting, HMIs play a critical role especially with Industry 4.0, or the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In the increasingly digital context, HMIs have become irreplaceable as a control plane for industrial operations and equipment on various scales.
For example, factory operators may use HMIs to monitor, manage and control autonomous machinery and production lines. On the other hand, HMIs become an essential part of system operability by enabling control of field-deployed devices that may be physically impossible to reach, such as in large-scale, long-range IoT!
Thus, as industries expand and individual asset management becomes near to impossible, HMIs have grown in importance to allow businesses to keep track of important elements such as performance, safety and maintenance!
HMI vs PLC vs SCADA
HMIs are often mentioned alongside Programming Logic Controllers (PLCs) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Systems and may even be mistaken to be the same. However, they actually represent distinct elements in industrial systems!
SCADA Systems refer to industrial control systems as a whole in a factory or a plant, and are responsible for handling complex backend operations. Embedded HMI components are required in SCADA systems to allow humans to easily interact with it!
However, for HMIs to in turn interact with the system, an additional component is required – the PLC! As the name suggests, Programmable Logic Controllers receive information from sensors connected in the system, process the data and perform outputs based on pre-programmed logic. The PLC transmits data to the HMI for display, while also accepting input for specific interventions or procedures like killing the system in the event of an emergency.
Benefits & Importance of HMIs
While the function of HMIs sound relatively basic, there are a few key reasons that an investment into an effective HMI can be a wise decision when designing industrial systems.
1. Essential for IoT at Scale
The Internet of Things is one of the hottest trends under the Industry 4.0 transformation. With up to thousands of devices’ connected in a single network, across up to long distances of 20 km or 12 miles, HMIs are considered an essential part of IoT systems, allowing conditions and data to be aggregated and managed from a single physical control plane.
2. Increase Productivity
HMIs provide operators with real time data and an intuitive understanding of production & operating conditions. Through visual tools such as graphs or references to data on the fly, HMIs enhance productivity by enabling more frequent and informed decision making on aspects like production optimisation and operational priority.
3. Reduce Costs
HMIs also allow operators to save costs by identifying idle resources and scaling appropriately to meet demand, hence minimising wastage. In addition, HMIs provide the means to monitor the condition of machinery for preventative or even predictive maintenance, allowing for the costs of complete failure or replacement to be significantly mitigated.
4. Improved Safety
HMIs are commonly used to implement safety measures for industrial systems. They can alert operators of operational hazards such as a leak, as well as identify when certain machinery are operating dangerously beyond their recommended conditions. Furthermore, HMIs often implement kill switches to mitigate damages in an emergency.
HMI: Industry Trends & Technologies
With different technologies being incorporated into HMIs, their functions and usefulness continues to evolve over time!
Touch Screens & Mobile Devices
In fact, touch screens and mobile devices are already commonly implemented in industrial HMIs today. Touch screens provide an intuitive way to interact with the graphical user interface of HMIs, improving operator productivity and reducing training costs. With modern smartphones carrying an impressive amount of processing capacity and power, some HMIs that do not require specific I/O may be built on software which can then be installed on personal devices, thus saving on hardware costs.
Cloud HMIs
A Cloud HMI is also known as a web-based HMI, and resides online or in the cloud. These HMIs are particularly useful to realise remote monitoring of industrial systems, which is expected to play an important role in the transformed landscape of the post-pandemic workplace. Cloud HMIs also allow businesses to utilise powerful computing resources for heavyweight data processing or analytics like machine learning. Such computers may not be suitable to operate in industrial environments due to temperature or size constraints.
Edge-of-Network HMIs
Edge-of-Network HMIs operate on a similar principle as Cloud HMIs with a key difference. Instead of a centralised cloud server, Edge-Of-Network HMIs utilise computing resources that are located on the edge, such as directly in production environments. These bring about several benefits, including lower latency, improved security, and reduced dependence on network connectivity!
You may wish to read our previous articles to learn more about edge computing:
- Edge AI – What is it and What can it do for Edge IoT?
- Cluster Computing on the Edge – What, Why & How to Get Started
Augmented & Virtual Reality
Further along the horizon, both augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) HMIs are expected to transform the way that HMIs are used. For example, AR safety glasses with HUDs (Head-Up Displays) can be used in place of the traditional tablet to provide guidance to a maintenance operator. A few benefits of this technology may include:
- Freeing of the operator’s hands to work more efficiently
- Reduction in probability for mistakes with contextual guidance
- Improved safety from a reduction in distractions
VR seeks to bring the benefits of AR to an even greater level by allowing users to interact with operational environments remotely in virtual environments. With advancements in robotics and wireless technologies like high speed 5G Radio Frequency communication, we may soon see VR being utilised in industrial settings!
Developing / Choosing a HMI
Returning to its fundamental definition, any device that allows a human to interact with a machine system or device qualifies as a HMI! To develop or choose a good HMI, however, requires a deliberate consideration of its design and operability qualities. Here are several factors which you may wish to consider when developing a HMI for your specific use case.
Form Factor
Deciding on the form factor of your HMI depends on the physical usage environment. How large does your display have to be to show critical data effectively? Will the HMI be handheld or installed on a mount? These are all factors that need to be balanced in the design of your HMI. For example, a large screen is great for monitoring operational parameters, but hardly easy to use for a field engineer that is required to perform more hands-on tasks!
I/O Peripherals & Accessories
As HMIs ultimately serve as the bridge between users and systems, it’s only natural that I/O should not be neglected! For example, Gigabit Ethernet connectivity may make or break a HMI in cases which require high speed, low-latency communications. On the other hand, you may wish to opt for HMIs with integrated crypto authentication modules for systems handling sensitive data that must be kept secure!
Alarm Strategy
HMIs are used to alert operators to conditions that require intervention, such as machinery breakdown or a safety breach. In operating environments where a few seconds make a difference, each alarm must be able to draw operator attention and be associated with a clear corrective action so that the situation can be resolved appropriately and in a timely manner.
Additional alarming guidelines and features include:
- Well-defined alarm colours according to safety conventions
- Distinct visual and auditory cues to draw attention as required
- Intuitive GUI navigation from broad alerts to detailed diagnostics
Ultimately, designing or choosing a good HMI for your use case requires careful thought for the personnel who will utilise it. When in doubt, holding a design review with your team to learn about their specific needs will be the most helpful for all stakeholders!
Introducing ReTerminal: The Next Generation Human Machine Interface
With the benefits to be reaped from a HMI, choosing the best option can be overwhelming. Look no further, as Seeed has just released the ReTerminal, your Next Generation Human Machine Interface!
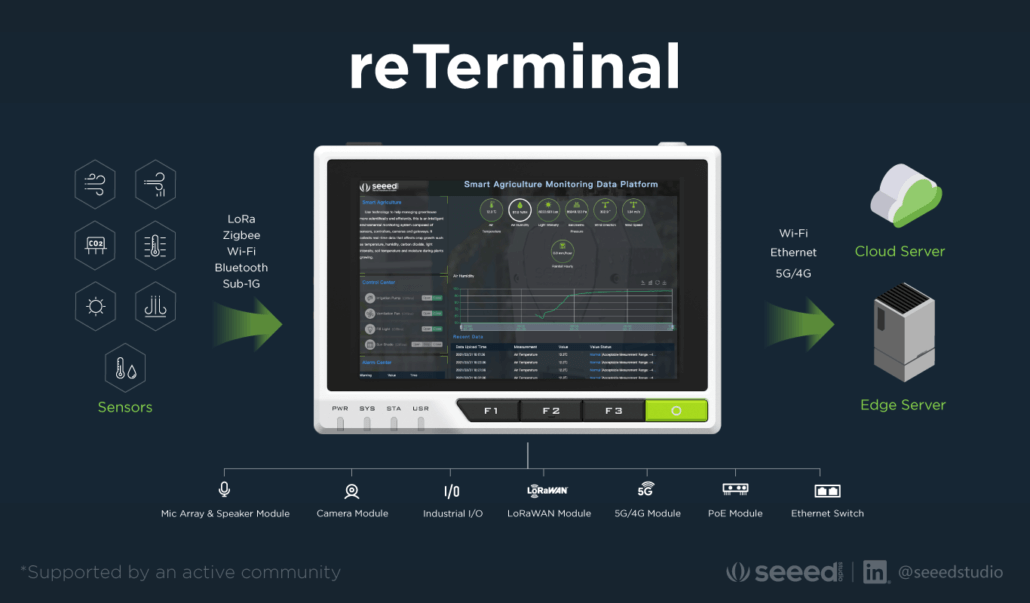
The ReTerminal is designed to be the most comprehensive and user friendly HMI yet with its 5 inch LCD display, allowing a variety of natural interactions through computer vision, touch, gesture and voice. Powered by the powerful and latest Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4, the ReTerminal is Machine-Learning ready and suitable for numerous use cases, thanks to its extensive range of I/O peripherals including Dual USB2.0 Type-A, Micro HDMI, MIPI Camera, GPIO, an expandable Industrial High-Speed Interface, and much more!
In terms of networking, the ReTerminal allows you to use Gigabit Ethernet, 4G, 5G LoRa, Sub-1G, WiFi and BLE in your applications, while keeping your data secure with its onboard Microchip ATECC608A Crypto-Authentication module – making it perfect for IoT!
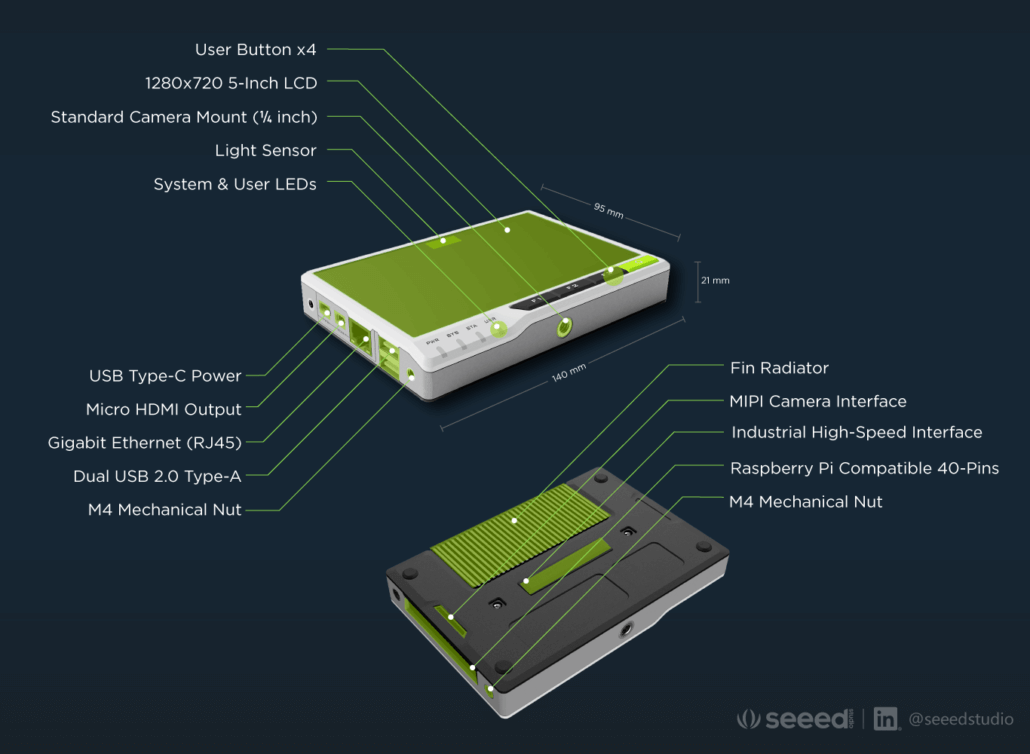
Product Features:
- Integrated modular design with high stability and expandability
- Powered by Raspberry Pi Computer Module 4 with 4GB RAM & 32GB eMMC
- 5-Inch IPS capacitive multi-touch screen at 1280 x 720 and 293 PPI
- Wireless connectivity with dual-band 2.4GHz/5GHz Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5.0 BLE
- High-speed expansion interface and rich I/O for more expandability
- Cryptographic co-processor with secure hardware-based key storage
- Built-in modules such as accelerometer, light sensor, and RTC
- Gigabit Ethernet Port and Dual USB 2.0 Type-A ports
- 40-Pin Raspberry Pi compatible header for IoT applications
Use the ReTerminal for Any HMI Application
The ReTerminal is packaged in a sleek and compact 140mm x 95mm form factor, and can be conveniently mounted through a standard M4 Mechanical Nut or Standard ¼ inch camera mount. Coupled with the great options for peripherals, connectivity and security, you can use the ReTerminal for nearly any HMI application!
For example, you can use the ReTerminal to monitor your devices in your personal IoT networks, or as management access nodes in smart cities, manufacturing and agriculture applications. Even if you don’t need a HMI, the ReTerminal still serves you well as an all-in-one carrier board to expand the possibilities of your Raspberry Pi Compute Module 4!
The ReTerminal will be available for preorder on the Seeed Online Store from the end of April. In the meantime, visit its product page to learn more, and be sure to register your interest to win $5 off as an early bird!
Summary
While HMIs are relatively simple components in industrial systems, they hold great potential to help us work smarter, safer, and better. Thus, putting in some effort to decide what features are needed in your HMI is definitely a worthy investment!
Alternatively, our brand new ReTerminal serves as a powerful all-in-one and expandable solution to meet the needs of any use case, while maintaining a sleek form factor for field deployment, so be sure to check it out!
To learn more about IoT, edge computing and what we do here at Seeed, you’re welcome to read any of the following articles!
- What is Industrial IoT? [Case Studies]
- What is Edge AI and What is Edge AI Used For?
- Edge AI – What is it and What can it do for Edge IoT?
- Cluster Computing on the Edge – What, Why & How to Get Started