Introduction to Buzzers: Piezo and Magnetic buzzers
Buzzers, they’re essentially an audio signalling device and can generally be found in our daily lives! They’re what wakes you up in the morning and reminds you something when you forgot to do so. In today’s article, we will be talking about buzzers!

We will be focusing on two types of buzzers: Piezo and magnetic buzzers since they’re more common as compared to the rest. With that said, let’s look at what will be covered:
- Overview of Buzzers
- Transducers and Indicators
- Key Specifications
- Applications of Buzzers
- Projects with Buzzers
Overview of Buzzers
What are buzzers?

Ref: Pinterest
Buzzers are electric sounding devices that generate sounds. Typically powered by DC voltage, they can be categorised as Piezo buzzer and magnetic buzzer. They come in different designs and uses as well, and based on that, they can produce different sounds!
Structure of the buzzers
There’s a difference in the working principle for Piezo and magnetic. Thus, we will first look at the difference in their structure:
Piezo Buzzer

As its name suggests, a Piezo-type buzzer’s core is the piezoelectric element. The piezoelectric element is made out of piezoelectric ceramic as well as the metal plate, they are held together in or piece by the adhesive.
Magnetic buzzer

As for the magnetic buzzer, it is mainly composed of the magnet, coil and the vibrating disk which is a ferromagnetic disk. This particular magnetic buzzer is an indicator which has the transistor.
Working Principle of the buzzers
Now that we’ve had a better look at Piezo and magnetic buzzers’ structures, we can move on to how they actually work:
Piezo buzzer

Due to the piezoelectric material, when an AC is passed through it, it’ll shrink and expand. This would then cause a vibration which would produce sound waves as you can see from the diagram.
Magnetic buzzer

In a magnetic buzzer, the current will be driven through the coil of wire and cause the vibrating disk to be attracted to it. The movement of the disk would produce the sound and it’ll return to its original state when there no current flowing through the coil of wire.
Variants of buzzers
Apart from the two main types of buzzers, they each also have sub-categories and other types of buzzers as well! So let’s take a brief look at them.
Electromagnetic buzzers
An electromagnetic buzzer consists of an oscillator, solenoid coil, magnet, vibration diaphragm, housing etc. Pretty much works the same as a magnetic buzzer, where they produce sound through magnetism, with a frequency of 2 kHz.
Mechanical buzzers

Mechanical buzzers are technically subcategories of electromagnetic buzzers, thus they consist of somewhat the same components. But what’s different is that the vibrating buzzer is mounted on the outer casing, instead of internally.
Electromechanical buzzers

Electromechanical buzzers are made out of electromagnet and bare metal disc. Works the same way as an electromagnetic and magnetic buzzer, it produces sound through the movement of the disc and magnetism.
Transducers and Indicators
Buzzers are actually designed to operate as transducers or indicators when they’re used in circuits. However, there are advantages and disadvantages when it comes to using indicators or transducers. So let’s look at each of their characteristics and differences:

Transducers
- An external driving circuit required
- Able to personalise frequencies or select multiple frequencies
- Complex to design-in
Indicators
- Has a built-in driving circuit
- Unable to select your frequencies, fixed
- Easy to design-in
Despite their differences, both transducers and indicators are able to produce continuous tones and slow/fast pulse sounds.
However, to do produce continuous tone, transducers need to supply a continuous fixed frequency square wave wile indicators need to supply continuous DC voltage. To produce slow/fast pulse sound, transducers need to supply square wave pulses of fixed frequency, while indicators to be alternatively switched on and off by applying PWM.
Key specifications of buzzers
- Type of buzzer – As we mentioned previously, there are two types of buzzers when used in circuits; transducers and indicators. Both have their different uses so pick your poison!
- Sound Pressure Level (SPL) – The deviation from atmospheric pressure caused by the sound wave. SPL is useful when comparing two different audio output, this would then indicate which is louder.
- Resonant Frequency – Refers to the frequency in which the buzzer vibrates.
- Frequency Response – A buzzer has different SPL for different frequencies, that also means that a buzzer produces different frequencies at different loudness.
- Operating Voltage – Piezo buzzers generally have a wider range of operating voltage while magnetic buzzers have a narrower operating voltage.
- Impedance – Refers to the electrical impedance, the ratio of an applied voltage to the current. This also varies with frequency.
Applications of buzzers
Electrical fire alarm

The fire alarm will only sound when a fire broke out so it’ll need to be loud and alarming to evacuate the people. Thus, a fire alarm would generally use s piezo buzzers. If you’re interested in making your own fire alarm, do check out our project below!
Microwave oven
/GettyImages-92928577-5a5e5ee45b6e240038e096f0.jpg)
I’m sure almost everyone has used a microwave oven before, where you set the timer and once the time is up, it’ll start beeping. Thus, a microwave oven uses a piezo buzzer as well just like the previous fire alarm. Since its purpose is to notify the user.
Before we jump into the fun projects you can do with buzzers, if you’re looking for a buzzer to experiment, Seeed does offer buzzers so do check it out if you’re interested!
Grove – Piezo Buzzer/Active Buzzer

Our Grove piezo buzzer makes it easy for anyone who’s interested to learn, as it simplifies the prototyping process with no soldering, or jumpers required! It has a resonant frequency of 2300±300Hz, sounds output of ≥85dB.
Here, we’re recommending the piezo buzzer since it is more versatile. Though if you’re interested in passive buzzer, do check out this and it is a Grove as well:
Grove – Passive Buzzer

With that said, let’s move on to our projects!
Projects with buzzers
How to Make a Fire Alarm
As we mentioned earlier, if you’re interested in building and installing a fire alarm at home, this is the project for you! It requires minimal materials and its simple enough to allow beginners to follow.
What you’ll need:
- Piezo buzzer // Grove – Piezo Buzzer/Active Buzzer
- 9V Battery & Snap
- PCB
- Fluorescent light starter
Sounds fun? Do check out the project for more details!
Control Volume of Piezo Buzzer- Circuits for Beginners
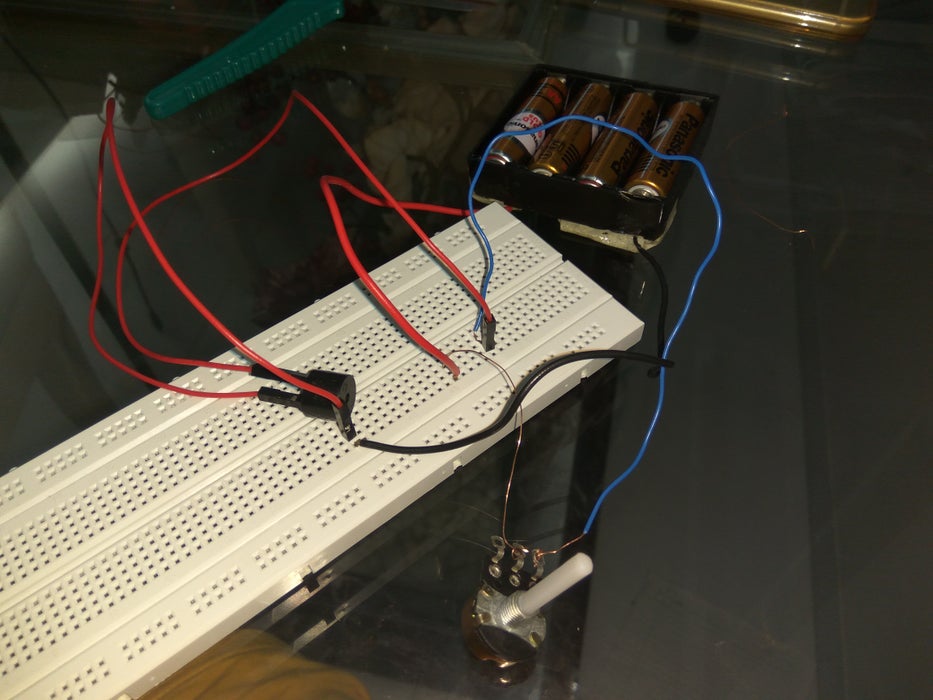
If you’re a complete beginner with electronics or a piezo buzzer, do check out this project. It’ll teach you all the fundamentals you need to learn about constructing a basic circuit with piezo buzzer and how to adjust the volume of it as well!
What you’ll need:
- 1 x Piezo buzzer // Grove – Piezo Buzzer/Active Buzzer
- 1 x 10k potentiometer
- 1 x Breadboard
- 2 x Female to male jumper cables
- 1 x 4 cell battery pack (with wires attached)
- 2 x Normal wires with both ends stripped
Learn the basics of using a piezo buzzer in a circuit by checking out this project!
Pocket Distance Alarm
During this Covid period, it is advised that we stand at least 1m apart from another person. Thus, this pocket distance alarm will definitely come in handy to help remind you and allow you to stay safe!
What you’ll need:
- Seeeduino XIAO
- Grove – LED pack
- Grove – Piezo Buzzer/Active Buzzer
- Grove – Time of Flight Distance Sensor(VL53L0X)
Sounds like something up your alley? Check out this project now!
Musical Keyboard using built-in Buzzer
Want to learn more about software like Micropython and Arduino? Using our Wio Terminal, you’ll be able to learn everything about Wio Terminal’s functions and passive buzzer, and how to turn Wio Termial into a musical keyboard through Ardupy by following along Lakshantha’s tutorial!
What you’ll need:
Try out this project if you’re interested in learning how to program your very own musical keyboard using only our Wio Terminal!
Summary
That’s all on buzzers! Did you understand the difference between piezo and magnetic buzzers better now? Buzzers are definitely one of the key components beginners need to learn before you move on to Arduino. Hope that you’ll be able to utilise buzzers and create more fun and interesting projects!
Once you’re able to understand how to utilise buzzers, we recommend:
Grove Beginner Kit for Arduino

New to Arduino? The Grove Beginner Kit for Arduino got your back! This kit is perfect for STEM teaching and beginners who purely want to learn about Arduino and coding, it brings you the simplest way to get started with Arduino. After you’re more familiar with Arduino, you can also take the modules out and use Grove cables to connect the modules.
Features:
- Arduino UNO compatible board (ATmega320p based Seeeduino Lotus) + 10 most commonly used Arduino modules
- Compatible with over 300 Grove modules
- Beginner-friendly! Step by step project tutorials provided.
- No breadboard and jumper cables required, all modules are pre-wired.
Hope that this would help you on your electronics journey! Happy experimenting!