Introduction to Measuring Instrument: What is a Multimeter?
The multimeter is a measuring instrument that is practically essential in electronics. Can’t figure out what went wrong in your circuit? Don’t fret! A multimeter would do just the job and help you troubleshoot this issue.
Before we can start learning about multimeters today, these are some basic concepts you should know before we can do so:
- Voltage: Difference in charge between the two points.
- Current: Flow of electrical charges.
- Resistance: Measure of opposition to the flow of current.
Should you need any recap with regards to these concepts, check out these blogs!
- What happens in an electric circuit: Voltage vs Current
- Basic Electronics: Alternating Current(AC) vs Direct Current(DC)
Putting that aside, we can now move on to what will be covered in this topic:
- Overview of Multimeter
- How to measure Voltage, Current and Resistance?
- Recommendations for Multimeter
- Projects with Multimeter
Overview of Multimeter
What is a Multimeter?
A Multimeter is known as a multitester or VOM (Volt-Ohm Milliammeter). It is an all-in-one electronic measuring instrument that combines several measurement functions. Thus, it’ll be able to troubleshoot issues with your circuit or electronic designs!
There are two types of multimeter, but a typical multimeter is capable of measuring voltage, current and resistance. We will go into more detail in the latter part of this guide.
A typical multimeter nowadays looks like this:
Types of Multimeter
Although we mainly use digital multimeters these days, as I briefly mentioned earlier, there are two types of multimeter:
- Analog
- Digital
Let’s talk about Resolution in multimeters before stating their differences: The resolution of a multimeter is the smallest part of the scale which can be shown, which is scale-dependent.
Analog Multimeter
The analog multimeters are more responsive to changes than digital multimeters, thus it is able to give a more accurate reading. However, because it is so sensitive, this makes it hard to read and gives delays.
Digital Multimeter
The resolution of a multimeter is often specified in the number of decimal digits resolved and displayed. Some digital multimeter is able to configure its resolution as well!
Parts of a Digital Multimeter
A Multimeter is made up of 3 main portions:
- Display: Measurements are displayed here
- Selection Knob: Allows you to select what to measure
- Ports: Where you plug in the probes

It should also come with probes, and note that the color does not matter!
How to measure voltage, current and resistance?
Continuity
Before we get into the measurements, it is important to know how to test the continuity of your circuit. Continuity allows you to detect bugs and troubleshoot your circuit.
To do so, turn your knob to this symbol:
This would allow a very small amount of current to flow without resistance. You can then proceed to touch the two probes together. If your circuit is connected, you should hear a continuous sound. If not, then it’s a sign for you to troubleshoot!
Note: Not all multimeter have this option, but most multimeter should be able to do so.
Measuring Voltage
All you have to do is plug in the probes and turn to the amount of voltage you require. Below is an example of how to measure a battery’s voltage:
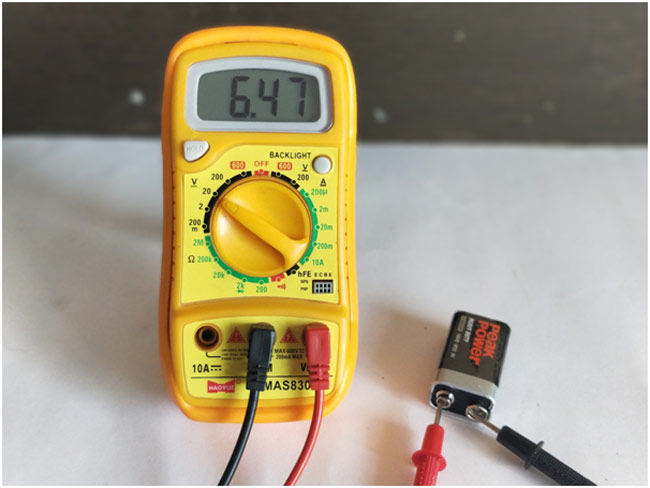
Note: Your red probe should be plugged into the positive terminal, do the same for the black probes. If not, you’ll get a negative reading.
Measuring Current
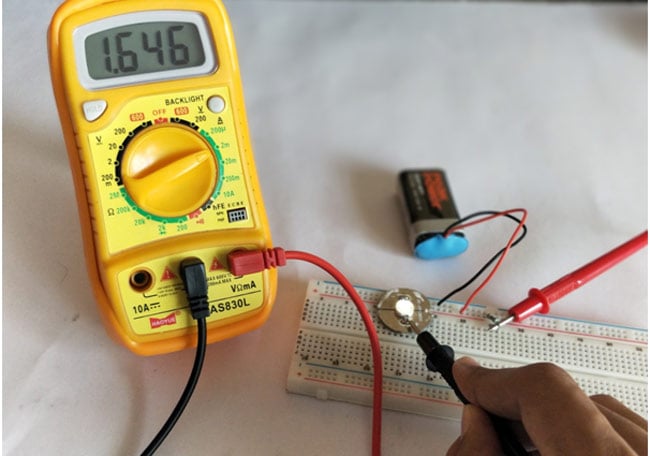
To measure current, you need to plug the probes in the opposite as to what you’ve done to measure voltage. This is because current should be measured in series. Thus it would look something like this:
Measuring Resistance
Your probes should be arranged as if you’re measuring current, just turn the knob to resistance symbol. All you need to do is choose the amount of voltage you need. It should look as such :
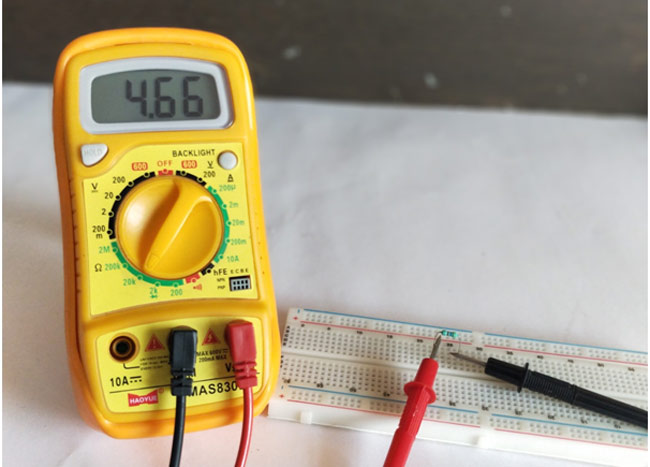

Note: You should never attempt to measure resistance in a circuit with resistors since the readings would not be accurate.
Recommendations for Multimeter
Now that we know how a multimeter works, I will be recommending 2 multimeters we offer in Seeed and hopefully, you will find the one that’s able to satisfy your needs!
Digital Capacitance Meter ($34.90)

Our Digital Capacitance Meter ($34.90) has a high measurement accuracy and a wide measurement range, which makes it durable and highly reliable. The multimeter is compact, pocket-sized and light-weight as well! Although this is the most basic multimeter out of the recommendations, this would definitely satisfy any beginner who is looking for a beginner-friendly multimeter!
What’s included:
- Digital Multimeter
- A pair of probe cables
- Measuring connector
- Black Bag

Features:
- Beginner-friendly multimeter
- High measurement accuracy, wide measurement range
- LSI application: Low battery indication, fast sampling
- Portable and pocket-sized
DT71 Mini Digital Smart Tweezers – LCR/ ESR Meter, Multimeter, SMD Tester with Built-in Micro Signal Generator ($59.00)

Our Mini Digital Tweezers is a tool for multi-function measurements with full differential input measurement. Thus, this is perfect for someone who wants something that functions more than a regular multimeter!
What’s included:
- DT71 Controller
- 2 x Tweezer Tips
- Test Arms
- Data Cable
- Carrying Case
- Safety Instructions
.jpg)
Features:
- Unique trinary structure: Controller, Testing arms, and Tweezer tips all in one! They are separable, combinable and replaceable as well.
- Lightly touch the top of the controller to operate! Includes intelligent functions such as automatic identification and Automatic shutdown.
- Various measuring types: resistance, voltage, inductance, diode etc.
- Dual built-in rechargeable lithium batteries = lasts up to 10 hours. Yet it only takes 2 hours to charge to full!
- Built-in miniature waveform signal generator: output waveform signals and helps to debug, provide maintenance for complex electronic systems as well.
- Automatically identify SMDs and distinguishes different components quickly.
- Portable and compact in size (comes in a carrier!)
- Equipped with OLED screen on the 360° rotatable controller, provides visibility at all angles with smart left/right-hand operation.
Using Multimeter in Projects
Potato Battery

Want to DIY your battery? Here’s a fun project you can try to light up a bulb using fruits or vegetables!
What you’ll need:
- 3 potatoes (or fruits!)
- 3x copper and zinc electrodes
- 6x Alligator Clips
- 3x Red LED
- digital multimeter
- Piezoelectric buzzer
Sounds interesting? Click here for more instructions!
How Bright Is Your Glow Stick?

Feel like experimenting with glow in the dark items? Look no further! This project allows you to measure the light given off by luminescent materials.
What you’ll need:
- Digital multimeter
- Photoresistor
- 2x Alligator clips
- Glass jar with lid
- Glow sticks
- Aluminium foil
- Black electrical tape
- Drill with a 1/4-inch drill bit to make a hole in the jar lid
Click here to check out their website for detailed instructions!
Summary
That’s all on multimeter! We discussed what is a multimeter, its usage and showed you some of our recommendations. Let us know if we helped you in any way! We hope you have a better understanding of multimeters after this!



