Basic Electronics: Electronic Load and Battery Testing
In a circuit system, the robustness of the power supply is extremely important. Therefore, we need to evaluate the power supply performance before use (i.e. whether it can maintain the stable power supply over time). In order to evaluate the power supply in all aspects, electronic loads will be used. But what exactly is an electronic load?
In this blog, I will cover the following topics:
- Introduction to Electronic Load
- Types of Electronic Loads: Capacitive, Inductive and Resistive
- Operation Modes of Electronic Load
- AC Electronic Load & DC Electronic Load
Introduction to Electronic Load
An electronic load could be any component in a circuit that consumes power or energy. Electronic loads are often used for power supply testing. There are many types of electronic loads, including DC power supplies, batteries, and AC power supplies.
Power Supply and Load
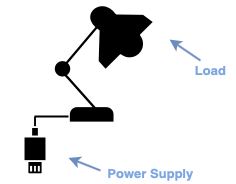
In a circuit, it is the power supply that supplies the electricity, and the power-consuming device connected to the power supply is called a load. For a lamp, the power supply is used to light a lighting appliance, and the lighted lamp is the load.
If the power supply cannot supply power to the load stably, the system will not work properly. Therefore, it is very important to test the performance and reliability of the power source.
Determine Testing Load
There are many kinds of power supply loads, they can be desk lamps with almost zero change in load or motors with large changes. For motors of the car, the load is relatively large when climbing a steep slope or carrying heavy stuff. Increased load means more power is required. However, it is easy to determine the conditions under which the load will change greatly according to the purpose of the motor.
As mentioned before, the load of the power supply changes frequently. Whether the power supply can withstand such load changes will only be known after evaluation. Without the load, there is no current output from the power supply, thus the testing is meaningless.
To test the performance of the power supply, electronic load is particularly important. But why we use simulated loads instead of actual load?
Why use simulated loads instead of actual loads?
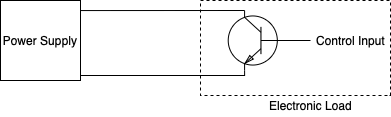
The object connected to the power supply during actual operation is called the actual load. The simulated load corresponds to the actual load. For actual loads, changing the test conditions is very difficult and inefficient. To increase efficiency as well as making things simple, the electronic load is used. By using a simulated load, the test conditions can be changed relatively simply to meet various requirements. Hence, it is more convenient to use an electronic load.
Types of Electronic Loads: Capacitive, Inductive and Resistive
Capacitive Load

In the capacitive load, the voltage and the current are out of phase, and the current wave is leading the voltage wave. The capacitor bank is the most commonly used capacitive load in our daily life. For capacitive load, the load is purely reactive hence it absorbs no average power. The current of a capacitive circuit is approximately zero after five time constants of the charging phase have passed in a DC circuit.
Inductive Load

Loads of electric motors are inductive loads, which utilize magnetic fields to do work. Same as capacitive load, the current and voltage are out of phase in inductive load and the load does not absorb average power. The difference is that in capacitive loads the current waveform leads the voltage waveform, but in inductive loads the current lags the voltage phasor.
Resistive Load

A resistive load means that the load is composed of any heating element. which blocks the flow of electrical energy and converts it into thermal energy. Common resistance loads include table lamps, ovens, kettles, etc. A resistive load absorbs power at all times. In a resistive load, the voltage is always in phase with the current.
Operation Modes of Electronic Load
There are four common operating modes of electronic loads, including constant resistance (CR), constant current (CC), constant voltage (CV) and constant power (CP).
Constant Resistance(CR)
In Constant Resistance(CR) operation, the load is a purely resistive load that draws a current proportional to the voltage.
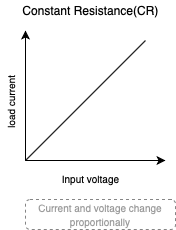
The resistive load can directly replace the resistors in the circuit. This method is suitable for testing startup conditions and current limiting characteristics of voltage and current sources.
Constant Current(CC)
In Constant Current(CC) mode, the output(load) current is at the specified set value, and it is independent of the input voltage.
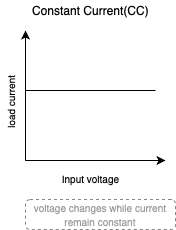
This method is widely used in the testing of power supplies such as switching power supplies as well as power consumption test.
Constant Voltage(CV)
In Constant Voltage(CV) operation, the electronic load will draw enough current to maintain a constant input voltage at source side.
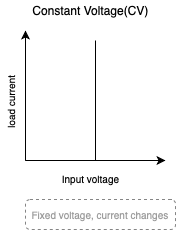
This can be used for testing chargers such as rechargeable batteries.
Constant Power(CP)
In Constant Power(CP) mode, the load current is depending on the set power. At this time, the product of the load current and the input voltage is equal to a set value, that is, the load power remains unchanged.
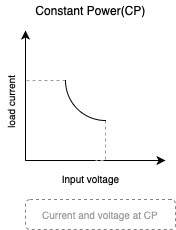
This method can be used to test the capacity of the power source.
AC Electronic Load & DC Electronic Load
DC Electronic Load: ZKETECH EBD-A20H
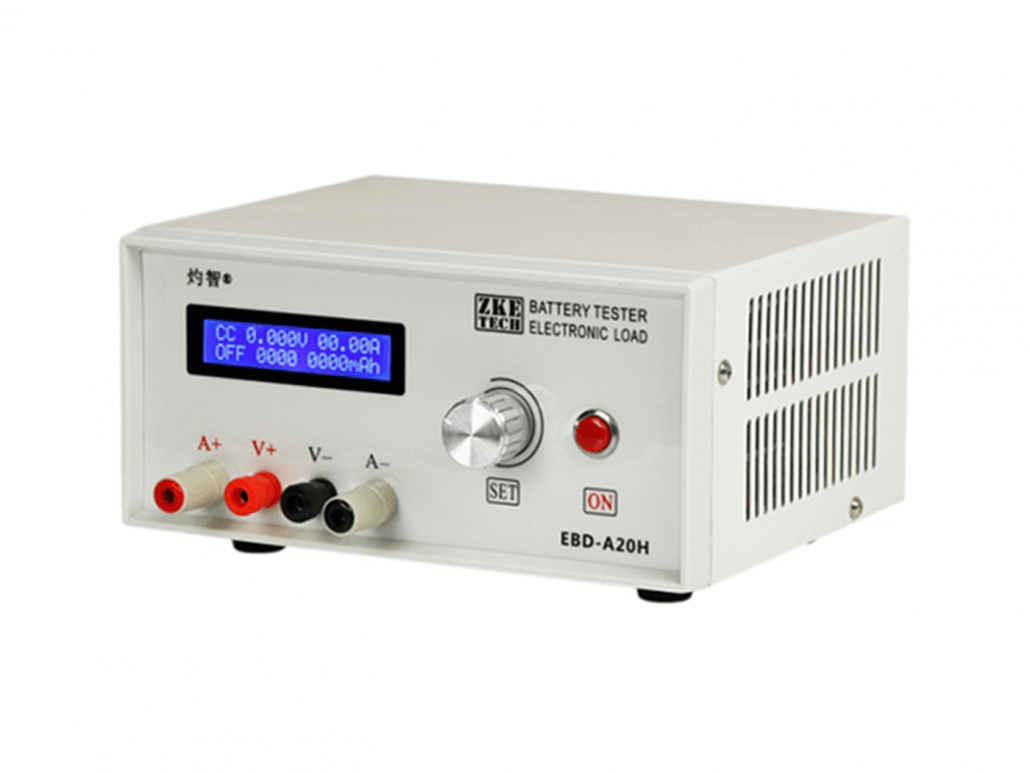

DC electronic load is used for testing DC output power and batteries. You can get a DC electronic load, ZKETECH EBD-A20H, which supports up to 30V/20A/200W from Seeed. ZKETECH EBD-A20H is a DC electronic load with multiple battery discharge modes and suitable for various battery capacity tests and power tests.
Simple Connection & Detailed Information Display
Believe it or not, you can simply get the desired result through a simple connection.
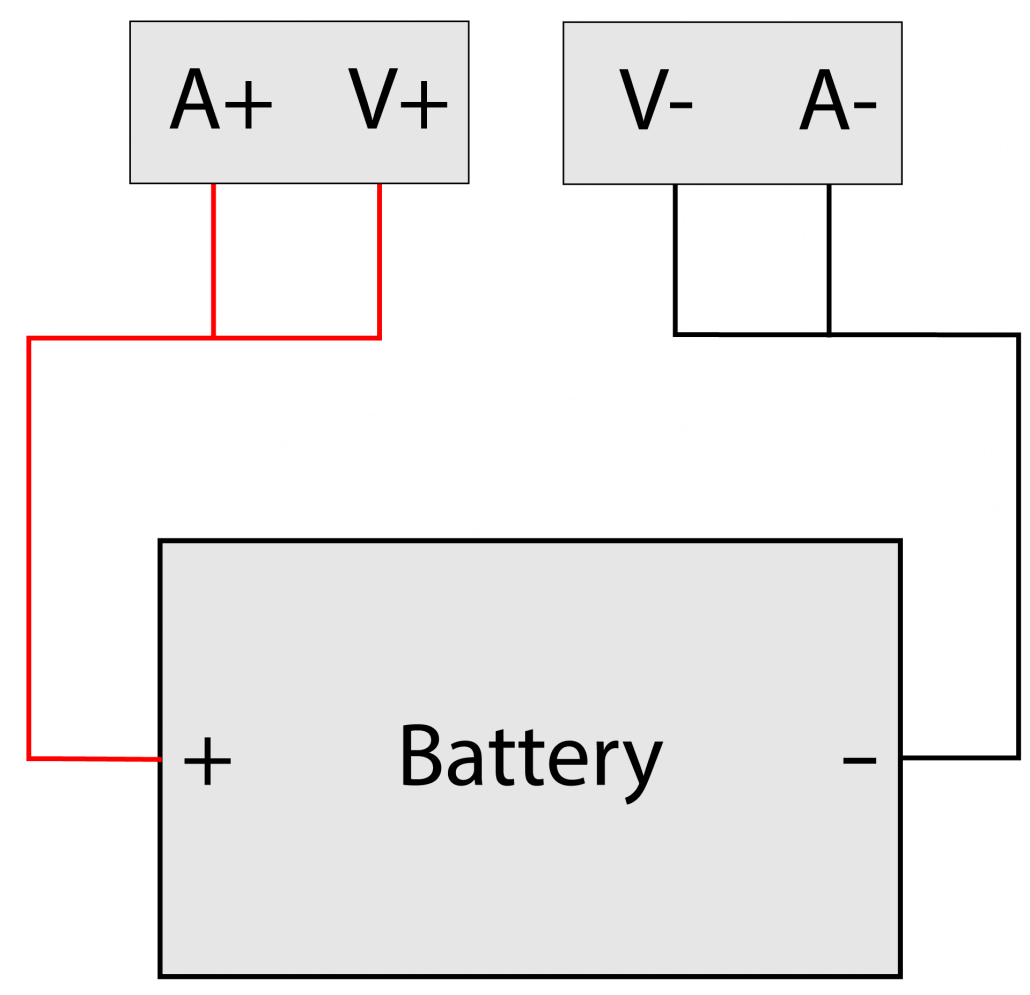
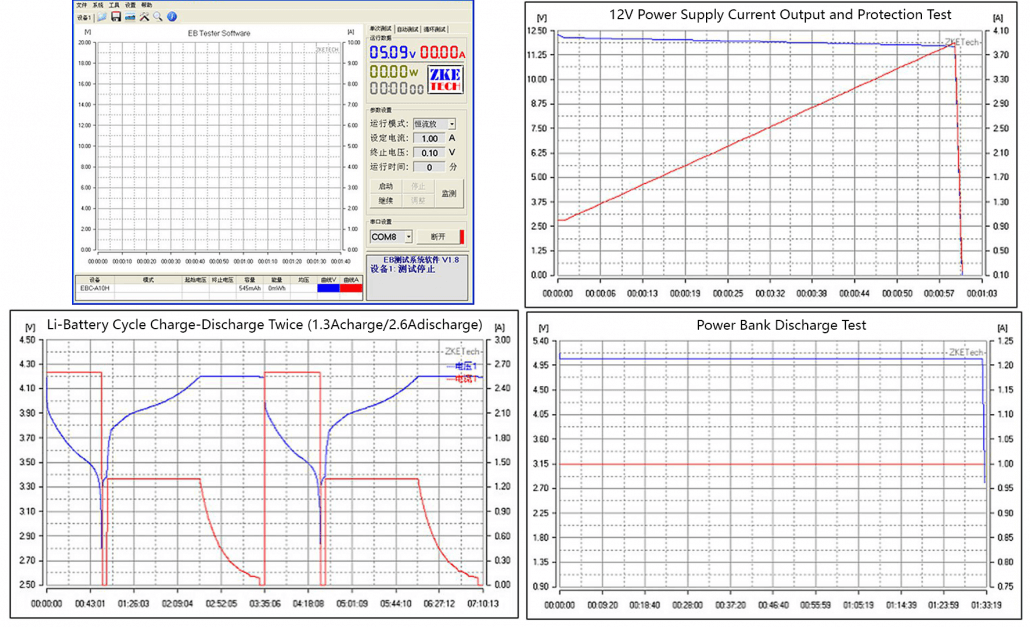
Is it too much effort for you to record each data point and plot them on paper? You don’t need to plot them on paper manually with ZKETECH EBD-A20H! A special software called “EB software” is used along with this device is here to help you! :p
The combination precisely displays the relevant test information. The software supports features such as curve drawing, computer control and can perform calibration benchmark tests, automatic current testing and firmware upgrades.
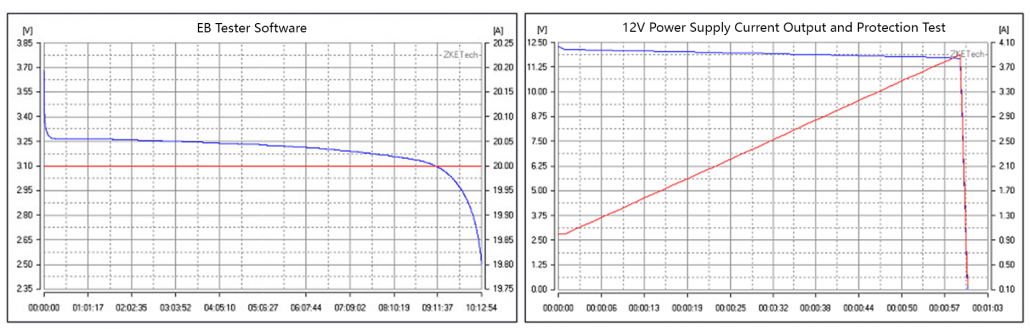
AC Electronic Load: ZKETECH EBC-A10H
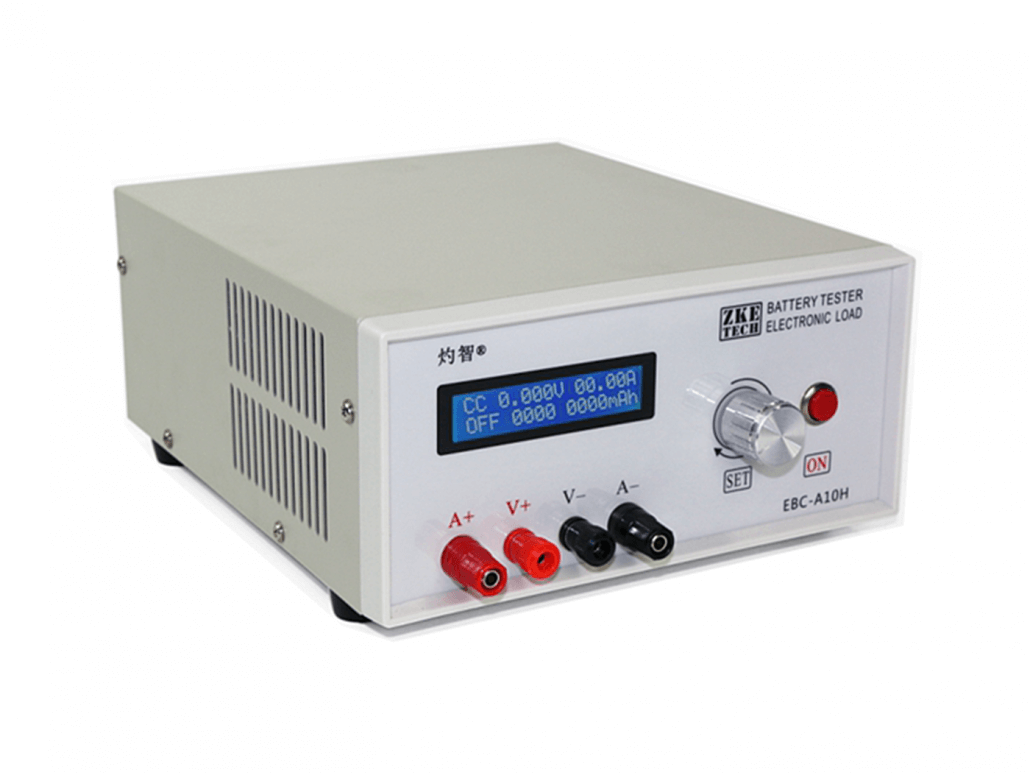

The AC electronic load differs from DC electronic load and it is used to test AC power and generators. Within a certain period of time, the direction (polarity) of the alternating current will change, DC electronic load is not applicable.
In Seeed, we offer you an AC electronic load supports up to 30V/10A/150W, which is ZKETECH EBC-A10H. ZKETECH EBC-A10H is an electronic load suitable for various types of battery charge and discharge testing and power performance testing.
Same as ZKETECH EBD-A20H, you can get the following graphs from EB software when you connect the power supply to ZKETECH EBC-A10H:
Summary
With the use of electronic load, the reliability and performance of various power source can be tested. DC electronic load is used for testing DC output power and batteries while the AC electronic load is for AC power and generators. Grab one and start testing your batteries!
Do you have any other basic electronics knowledge that you are interested in, please feel free to let us know in the comments section below!