TDS in Water – What is TDS and How to measure TDS in water with Arduino?
TDS which stands for total dissolved solids are often found in water as water is a good solvent that picks up impurities easily. But what is TDS? Should you be concerned? How do you measure the amount of TDS in your water?
No worries as today, we will answer all these questions you have about Total Dissolved Solids. This guide will cover:
- What are Total Dissolved Solids
- TDS in water – Should you be concerned?
- TDS Water Chart
- Measuring TDS in water with the Arduino
- How do you reduce or remove TDS in water?
What are Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)?
Dissolved solids refer to any inorganic and organic minerals, salts, metals, cations (eg. calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium) or anions (eg. carbonates, nitrates, bicarbonates, chlorides) dissolved in water. Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) is a measurement of the total concentration of dissolved solids in the water.
How do these solids end up in water?
The primary source for TDS in water normally originates from natural sources, sewage, residential run-off, industrial wastewater, chemicals used in the water treatment process and also the plumbing and piping used to transport water. A high amount of TDS can also be due to natural environment factors like mineral springs, carbonate deposits, salt deposits, etc.
How are they different from TSS (Total Suspended Solids)?
TDS are different from TSS (Total Suspended Solids). For TDS, they are solids that are smaller than 2-micrometer pores while TSS are bigger than that and yet are indefinitely suspended in water.
Why measure TDS in the water?
By measuring the amount of TDS in the water we are able to qualitative measure the number of dissolved ions and gives us an indication of the general quality of the water. However, it does not provide us insight into specific water quality issues like elevated hardness, salty taste or corrosiveness.
TDS in water – Should you be concerned?
Oh no! There is a high amount of TDS in my water, is it a health hazard?
No! Luckily, an elevated total dissolved solids concentration does not pose as a health hazard at normal levels. In fact, many of your mineral waters have a high level of dissolved solids due to their sources.
TDS is not considered a primary pollutant and is a secondary drink water standard and it is regulated as it is an indication of aesthetic characteristics of drinking water and used as an aggregate indicator of the presence of a broad array of chemical contaminants.
However, a high level of TDS may cause the taste of water to be bad. This is as the concentration of dissolved ions may cause the water to taste bitter, acidic, salty, or brackish taste. For example, when the TDS contains a high amount of Cations combined with carbonates like CaCO3, it will cause the water to have a bitter taste and when Cations are combined with chlorides like NaCl, it will cause the water to have a salty taste.
Due to the high levels of dissolved ions as well, it may result in scale formation and interfere and decrease the efficiency of water-powered equipment like your water heater.
It can also affect normal household chores like washing clothes as high TDS in water can fade the colour of your clothes and also cause a buildup in your sinks, tubs and faucets. Even when cooking, using high TDS water may alter the taste of your food as well. In pools and spas, TDS levels must be monitored to prevent maintenance problems. Own a hydroponic garden? Using TDS can also tell you the nutrient concentration in a hydroponic solution.
One thing to note that while TDS may only be an aesthetic and technical factor, but a very high concentration of TDS can have harmful effects as they are indicators of harmful contaminants such as iron, manganese, sulfate, bromide, and arsenic that can be present in water which can pose as health hazards and cause serious health problems especially for children as they are much more sensitive to contaminants as their immune systems have not been fully developed. High levels of TDS in water is possible due to the excessive dissolved solids added to the water due to human pollution and also runoff and wastewater discharges.
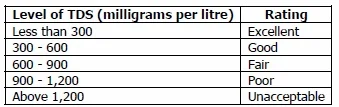
TDS Water Chart
So what level of TDS is good or acceptable? In a study by the World Health Organization, a panel of testers came up with a chart about the preferable level of TDS in water:
Here is also another table on how much TDS is present in your average tap water:

Measuring TDS in water with the Arduino
Now that you know what is TDS, its impact and how it may affect you, you are worried and want to measure the level of TDS in your water. But how? Well, normally TDS are measured in a laboratory where a sample will be filtered, dried and heated to find out how much TDS is present.
However, without all these equipment, how do we measure TDS easily and most importantly, in a cost-effective manner? Well, the solution will be measuring TDS using our Grove – TDS Sensor/Meter For Water Quality (Total Dissolved Solids) together with an Arduino.

How this TDS sensor works is that it is an electronic pen that is able to measure the conductivity of the water as the electrical conductivity of water is directly related to the concentration of dissolved ionized solids in the water. Ions from the dissolved solids in water create the ability for that water to conduct an electric current, which can be measured by this TDS sensor.
Alright you know how it works and what it does, here is a step by step guide to teach you how to measure the level of TDS in water with the Arduino and the sensor.
What do you need?
- Arduino Uno Rev3 / Seeeduino V4.2
- Base Shield – Optional, To make connections simpler
- Grove – TDS Sensor
Step by step instructions on how to use the TDS sensor with the Arduino
Step 1: Connect all the hardware
- Firstly, plug in the Grove – TDS Sensor to A0 port of the Base Shield
- Next, plug the Base Shield into the Seeeduino board
- Lastly, connect the Seeeduino to a PC via a USB cable.
- Your connection should something like this currently:

Step 2: Copy and upload code
- Open Arduino IDE and create a new file. Afterward, copy the following code into the new file:
#define SERIAL Serial
#define sensorPin A0
int sensorValue = 0;
float tdsValue = 0;
float Voltage = 0;
void setup() {
SERIAL.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
Voltage = sensorValue*5/1024.0; //Convert analog reading to Voltage
tdsValue=(133.42*Voltage*Voltage*Voltage - 255.86*Voltage*Voltage + 857.39*Voltage)*0.5; //Convert voltage value to TDS value
SERIAL.print("TDS Value = ");
SERIAL.print(tdsValue);
SERIAL.println(" ppm");
delay(1000);
}- Upload the demo. If you do not know how to upload the code, you can check out our guide on how to upload code
Step 3: Monitor Results
- Open the Serial Monitor of Arduino IDE by clicking Tool-> Serial Monitor. Or tap the Ctrl+Shift+M key at the same time.
- Set the baud rate to 9600.
- Place the electric pen in the water and you should see results on your monitor like this:

Annnnnd you are done! You can also add an LCD to the project and start monitoring the amount of TDS in your water everywhere you go like this:
How do you reduce or remove TDS in water?
Now that you’ve just measured the amount of TDS in your water, how do you reduce or remove them now you know that there is a high level of TDS present?
Here are some ways you can reduce and remove TDS in your water where you can also choose to combine the various water purification technologies to better reduce the amount of TDS in water.
Distillation

This process involves boiling to produce vapor. When water boils, it produces steam which rises to a cool surface and condensed back into liquid form. The dissolve salts would not vaporize and remain in the boiling solution.
Reverse Osmosis
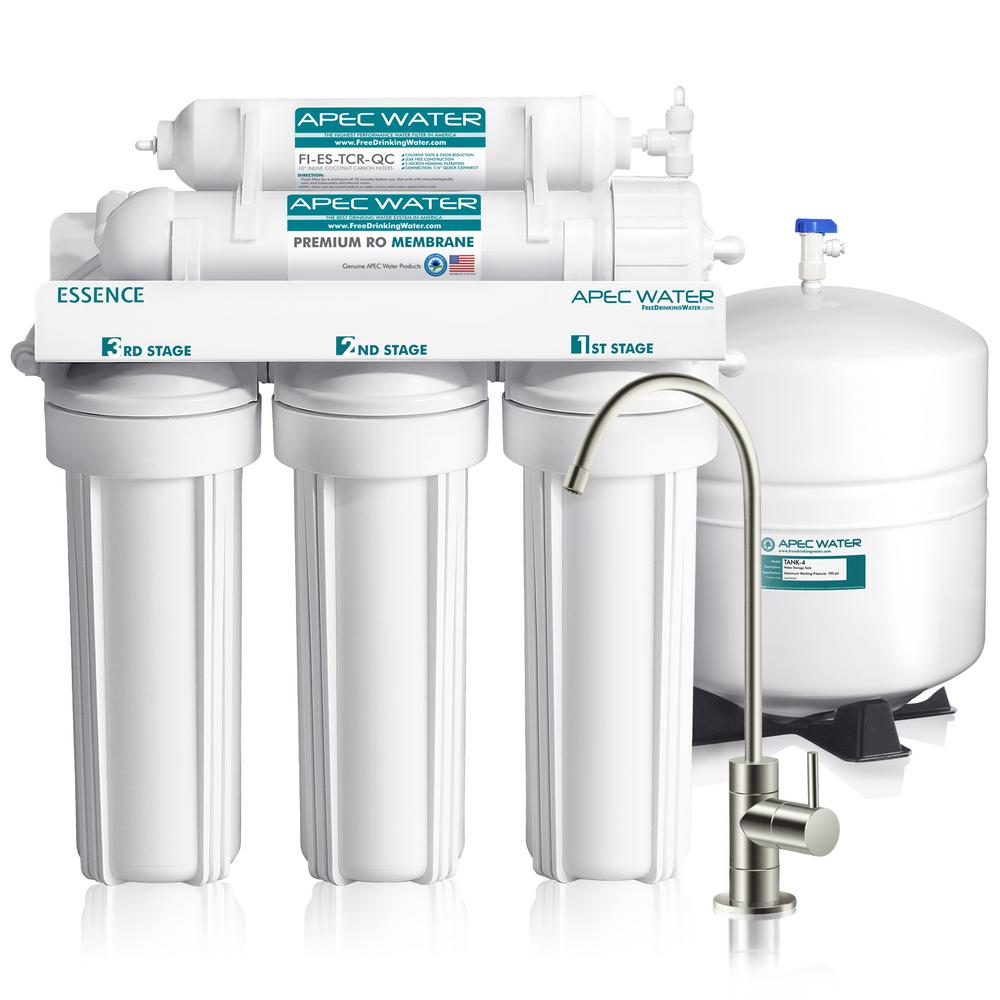

Reverse osmosis is also able to remove TDS as they force the water under pressure through a synthetic membrane. The membrane has microscopic pores which will allow only very tiny molecules to pass through which filters your water. As molecules such as dissolved metals and salts are large compared to the water molecules, water is able to squeeze through the membrane pores while leaving the dissolved solids behind.
Deionisation

In deionization, water will be passed through a positive and negative electrode. The ion-selective membranes enable the positive ions to separate from the water and move towards the negative electrode which get you de-ionized water with high purity. However, the water will be first passed through a reverse osmosis unit first in order to remove the non-ionic organic contaminants.
Summary
Despite an elevated total dissolved solids concentration not posing as a huge health hazard, at high levels, it can still cause health problems. In addition, high levels of TDS in water can also cause aesthetic problems or nuisance problems like a buildup in your sinks.
Do not know whether you need a water purification system? Well, we recommend getting your drinking water tested first with our Grove – TDS Sensor/Meter For Water Quality (Total Dissolved Solids) to determine the amount of TDS in your water before deciding whether there is a need to purchase a water treatment system!