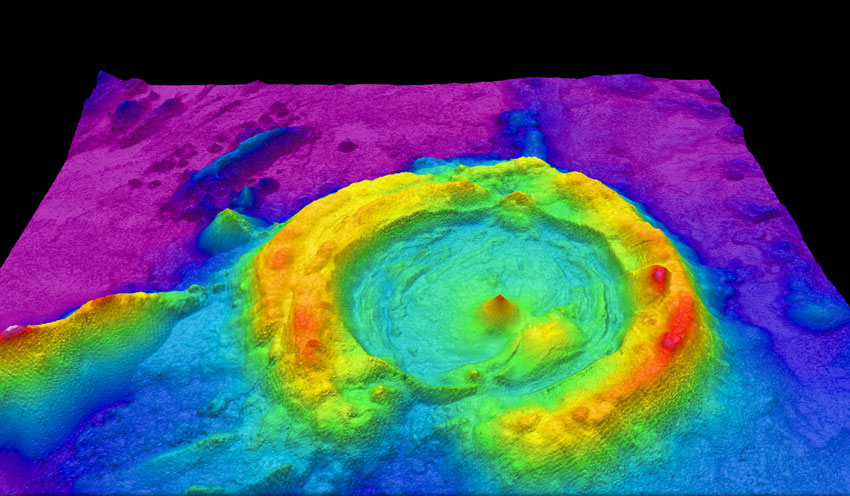
What is a LiDAR Sensor? – Technology, Uses, Projects

LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging is a popular remote surveying method used to measure the exact distance of an object on the earth’s surface. But what exactly is it? How does LiDAR works? What are their uses? No worries, as we will answer all your questions through this guide today.
Today, this guide will cover:
- How does LiDAR Technology works?
- Types of LiDAR systems
- LiDAR Sensor Examples
- LiDAR Applications
- LiDAR Projects to get you started
Without further ado, let us jump right into our first point:
How does LiDAR Technology work?
LiDAR technology is an active remote sensing system which means that the system itself generates energy which will be light in the form of a rapidly firing laser to measure ranges and the exact distance of an object on the Earth’s surface.
A LiDAR sensor has 3 primary components:
- Laser
- Send out and transmit pulses
- Scanner
- Receive and record the time delay between light pulse transmission and reception to calculate elevation values.
- Specialized GPS receiver
- Gives the location of the system with the LiDAR sensor
Similar to a “time of flight” mechanism, it works by firstly illuminating the target with the laser light and measuring the reflected light with a sensor where the distance of the object is deduced using the speed of light to calculate the distance traveled accurately. In addition, the differences in laser return times and wavelengths are then used to make precise digital 3D representations and surface characteristics of the target and visually map out its individual features.
With the laser return time, LiDAR is able to measure the exact distance in a short time given the speed at which light travels. Here is the formula which analysts use to arrive at the precise distance of the object:
(Speed of light x Time of flight) / 2
Here is an example of what LiDAR is able to do:

As you can see, the LiDAR technology is able to generate precise and accurate information about a road structure and identify obstacles to avoid collision.
LiDAR technology is similar to radar and sonar technology which used radio and sound waves. However, LiDAR technology is more precise compared to them as they are only able to plot the location of an object from a distance while LiDAR is able to generate precise digital 3D representations. This makes them suitable for up close and personal dynamics in various applications like autonomous vehicles.
To end off how LiDAR works, here are some examples in pictures of what LiDAR can do:


Types of LiDAR Systems
LiDAR systems are divided further into two different types based on their functionality:
Airborne LiDAR
- This is when a LiDAR system is installed on an aircraft during a flight to collect data and create 3D models of the landscape. As they are precise and accurate, they are used to create digital elevation models.
- They can be used to map land, measure seafloor, riverbed elevation and many more
- Airborne LiDAR is further split into two categories:
- Topographic
- Bathymetric
Terrestrial LiDAR
- Unlike airborne LiDAR, terrestrial LiDAR systems are either stationary or mobile. They can be installed on moving vehicles or tripods on the ground to collect accurate data.
- They are often used for conventional topography, monitoring cultural heritage documentation and used for observing roads, analyzing infrastructure and many more.
- Terrestrial LiDAR is further split into two categories:
- Mobile LiDAR
- Static LiDAR
LiDAR Sensor Examples
Here at Seeed, we offer a variety of LiDAR sensors. Here are a few of our favourites for those just starting out on LiDAR technology!
TFmini Plus – ToF LIDAR Range Finder

- This is a small size, low power consumption, single point short-range LiDAR sensor.
- TFmini Plus is a distance sensor of LIDAR which can emit near-infrared ray and measure the phase difference between the emitting ray and reflected ray to calculate the distance through ToF.
- Because of the LIDAR principle, it is hard to give an accurate distance between the transparent objects like water or glass. However, it is still a sensitive distance sensor in measuring the moving object and calculate the distance between the object and TFmini in real-time.
- This distance sensor leaves I2C and UART interface for developers and you can simply plug TFmini through the TTL to USB converter to the PC and get the distance data on your computer.
- As for the software, there is a test software upper computer software of TFmini that you can download to observe the distance changing when the object is moving in real-time.
- Interested in more details? You can check out the datasheet.
- Here is a video of the TFmini Plus in action:
Seeedstudio Grove – TF Mini LiDAR

- The TF Mini LiDAR is based on ToF (Time of Flight) principle and integrated with unique optical and electrical designs, so as to achieve stable, precise, high sensitivity and high-speed distance detection.
- ToF is the abbreviation of Time of Flight technology, and its operating principle is as follows: a modulated near-infrared light is sent from the sensor and reflected by an object; the distance to the object to be shot can be converted with the sensor by calculating the time difference or phase difference between the light sending and the light reflection, so as to produce the depth information.
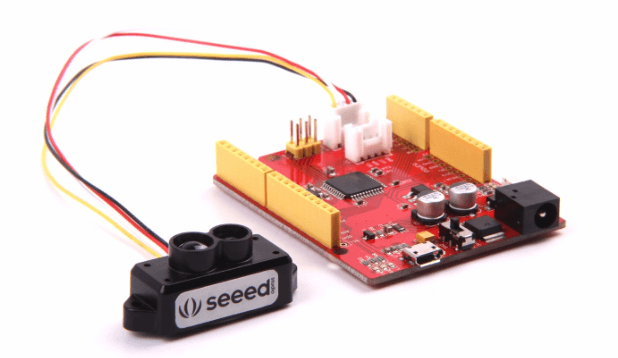
- Using one of our Seeeduinos? You can easily plug them in through one the Grove Serial Interfaces and get started!
- Here is a video of it in action:
Intel RealSense LiDAR Depth Camera L515

Require a small yet high performing LiDAR sensor? This new Intel RealSense LiDAR Depth Camera L515 will be perfect!
The Intel® RealSenseTM LiDAR Depth Camera L515 is Intel’s first release of a LiDAR camera enabling highly accurate depth sensing in a small form factor.
Small enough to fit in the palm of your hand, the L515 is 61mm in diameter and 26mm in height. At approximately 100g, it’s designed to be easily situated on any system, or attached to a tablet or phone. It also runs at less than 3.5W, considerably lower than competing time-of-flight (TOF) solutions. As all of the depth calculations run on the device, it also has low host compute requirements, resulting in true platform independence.
TFmini S LiDAR module – Short-Range ToF LIDAR Range Finder

- TFmini S LiDAR module – Short-Range ToF LIDAR Range Finder is a distance sensor of LIDAR which can emit near-infrared ray and measure the phase difference between the emitting ray and reflected ray to calculate the distance through ToF.
- Because of the LIDAR principle, it is hard to give an accurate distance between the transparent objects like water or glass. However, it is still a sensitive distance sensor in measuring the moving object and calculate the distance between the object and TFmini in real-time.
- This distance sensor leaves I2C and UART interface for developers and you can simply plug TFmini through the TTL to USB converter to the PC and get the distance data on your computer.
- As for the software, there is a test software upper computer software of TFmini that you can download to observe the distance changing when the object is moving in real-time.
- Interested? You can check out its datasheet for more information.
RPLiDAR A1M8 360 Degree Laser Scanner Kit – 12M Range

- RPLIDAR A1 is a low cost 360-degree 2D laser scanner (LIDAR) solution developed by SLAMTEC. The system can perform a 360-degree scan within a 6-meter range. The produced 2D point cloud data can be used in mapping, localization and object/environment modeling.
- RPLIDAR A1’s scanning frequency reached 5.5 Hz when sampling 360 points each round. And it can be configured up to 10 Hz maximum.
- RPLIDAR A1 is basically a laser triangulation measurement system. It can work excellent in all kinds of indoor environments and outdoor environment without sunlight.
- If you require a different range for your LiDAR project, you can check out:
LiDAR Applications
With LiDAR accuracy, precision and flexibility, they can be applied to many industries. Here are a few examples:
Autonomous Vehicles

When it comes to autonomous vehicles, a LiDAR sensor will definitely be needed. LiDAR acts as an eye for the vehicle for obstacle detection and avoidance to navigate safely. With rotating laser beams, they have a precise and accurate 360 view to avoid obstacles and collision.
Agriculture

LiDAR technology can also be used in the agriculture industry to create a precise 3D elevation map of a particular land to reveal slopes and sun exposure of the land. With this, they can help with analysis of yield rates, crop scouting for weed control, and seed and fertilizer dispersions.
Oceanography
With water penetrating green light of the LiDAR, you can find out the depth of a river or the ocean surface to locate any object in the case of a maritime accident or for research purposes. It can understand the depth, width, and flow of water for monitoring purposes.
LiDAR Projects to get you started
To get you off the ground with LiDAR, here are a few project examples which you can follow to learn more about LiDAR and apply them:
LiDAR Arduino Laser Harp
Do you want to build a musical instrument that you can play in the air? With the LiDAR and the Arduino, you can do just that!
What do you need?
- RPLiDAR A1M8 360 Degree Laser Scanner Kit – 12M Range
- Seeeduino Mega
- Grove – Rotary Angle Sensor
- Resistor 10k ohm
- Capacitor 1 µF
- Microsoft Visual Studio Code Extension For Arduino Software
Interested? You can find the full tutorial on Hackster.io by Doctor Volt!
Intelligent Dinosaur Robot
Want to make an intelligent dinosaur robot that can walk, with a smart voice assistant like Alexa or Google Assistant? Why not try this dinosaur robot that is made with the Raspberry Pi, Arduino and LiDAR!
What do you need?
- Grove – Servo
- Seeedstudio Grove – TF Mini LiDAR
- Seeeduino Nano / Arduino Nano v3
- Grove – 16-Channel PWM Driver (PCA9685)
- ReSpeaker 2-Mics Pi HAT
- Raspberry Pi Zero W
- Raspberry Pi Camera Module V2
- 18650×2 Battery Holder
- Triple Axis Accelerometer and Gyro Breakout – MPU-6050
- 5 volt UBEC
- Arduino IDE software
- Raspbian Software
- Google Assistant SDK
- Amazon Alexa Voice Service
- Laser Cutter
- 3D printer
Interested? You can find the full tutorial by Jacquin Buchanan on Seeed Studio Project Hub!
LiDAR Radar

With the LiDAR capabilities, you can of course also create a radar with it together with the Arduino!
What do you need
- Seeeduino V4.2 / Arduino Uno Rev3
- Seeedstudio Grove – TF Mini LiDAR
- 2 x Grove – Servo
- Grove – 16-Channel PWM Driver (PCA9685)
Interested? You can find the full tutorial by kd8bxp on Instructables!
Summary
That’s all for What is a LiDAR Sensor? – Technology, Uses, and Projects! Through this guide, I hope that you have learned more about LiDAR technology and its functions!
What do you think of the LiDAR sensor? How would you use it in your projects? Let us know in the comments down below!
If you are interested in more LiDAR products, you can check out our LiDAR series where we offer over 10 types of LiDAR sensors for your project needs!
If the LiDAR sensor isn’t what you are looking for in the distance sensor category, you can check out our guide on the different types of distance sensor and how to select one that suits your project!