All about Proximity Sensors: Which type to use?
Inductive, Capacitive, Ultrasonic, IR? These are the common types of proximity sensors used today for varying applications. Picking one that’s easily connectable, accurate, and reliable is very much important for fulfilling your intended usages.
In this guide, I’ll cover the various proximity sensor types, their uses, and price, with recommendations to make your decision an easier one!
This guide will cover the following components:
- What are proximity sensors?
- Types of Proximity Sensors
- How to pick a Proximity Sensor
- Comparison between different Proximity Sensors
What are proximity sensors? Overview

Proximity sensors are sensors that detect the movement/presence of objects without physical contact and relay that information captured into an electrical signal. It can also be defined as a proximity switch, a definition given by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) to all contactless detecting sensors
- Sounds complex? A proximity sensor simply means; A sensor that detects, captures, and relays movement information of objects without any physical contact!
Where are Proximity Sensors used?
Proximity Sensors are widely used in industrial and manufacturing applications, especially for safety and inventory management applications. In an automated production line, for example, it is used for object detection, positioning, inspection and counting. It is also used for part detection in an industrial conveyor system.
Proximity sensors can also be found in consumer devices. In smartphones, proximity sensors are used to detect if a user is holding their phone near their face. They are also used as capacitive touch switches on consumer electronics products.
It is also used for many other different applications such as a diffuse sensor in a public washrooms or a collision detection sensor for robots!
Proximity Sensor Features
To further understand what proximity sensor is all about, we’ll take a look at its features. The following is its features, with some uniquely seen as compared to traditional optical/contact sensors:
Contactless sensing
Contactless proximity sensing allows for detection without touching the object, ensuring object stays well-conditioned
Unaffected by surface conditions
Proximity sensors are nearly unaffected by surface colors of objects since it mainly detects physical changes
Suitability for wide range of applications
Proximity sensors are suitable for damp conditions and wide temperature range usage, unlike your traditional optical detection.
Proximity sensors are also applicable in phones as well, be it your Andriod or IOS devices. It consists of simple IR technology that switches on and off display accordingly to your usage. For example, it turns off your display when a phone call is ongoing such that you wouldn’t accidentally activate something while placing it near your cheeks!
Longer service life
Since a proximity sensor uses semiconductor outputs, there are no moving parts dependent on the operating cycle. Thus, its service life tends to be longer as compared to other sensors!
High speed response rate
Compared to switches where contact is required for sensing, proximity sensors offer a higher-speed response rate.
Types of proximity sensor
Now that we’ve understood what proximity sensors are, we’ll dive further into the various types; each well suited to its specific applications and environments.
Ready? Here’s the rundown of the different proximity sensor types!
Inductive Proximity Sensors
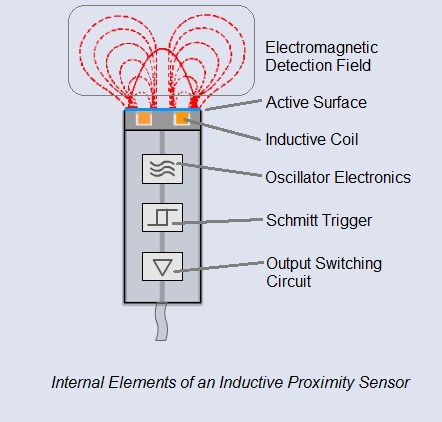
Inductive proximity sensors are contactless sensors used to only detect metal objects. It’s based on the law of induction, driving a coil with an oscillator once a metallic object approaches it.
It has two versions and comprises of 4 main components:
Versions:
- Unshielded: Electromagnetic field generated by the coil is unrestricted, allowing for wider and greater sensing distances
- Shielded: Electromagnetic field generated is concentrated in the front, where sides of the sensor coil are covered up
Components:
- It comprises of 4 main components as seen in the picture; Coil, Oscillator, Schmitt Trigger, and output switching circuit
How do Inductive Proximity Sensors work?
- An alternating current is supplied to the coil, generating an electromagnetic detection field
- When a metal object comes closer into the magnetic field, eddy currents build-up, and result in coil inductance changes
- When coil inductance changes, the circuit that has been continuously monitoring, will trigger the sensor’s output switch
*Note: Even when a target is not present, inductive sensors continue to oscillate. The switch is only triggered when an object is present.
Common applications:
- Industrial usages
- Production automation machines that count products, product transfers
- Security usages
- Detection of metal objects, armory, land mines, etc.
Advantages of inductive proximity sensors
- Contactless detection
- Environment adaptability; resistant to common conditions seen in industrial areas such as dust and dirt
- Capable and versatile in metal sensing
- Considerably cheap when it comes to price
- No moving parts, ensuring a longer service life
Disadvantages of inductive proximity sensors
- Lack in detection range, averaging a max range of up to 80mm
- Can only detect metal objects
- Performance can be affected by external conditions; extreme temperatures,
cutting fluids or chemicals
Grove – 2-Channel Inductive Sensor (LDC1612)

Here at Seeed, we offer this inductive sensor, where it enables the performance and reliability benefits of inductive sensing to be realized at minimal cost and power.
Expanding beyond just proximity sensing, its Arduino compatible with the capability of remote sensing applications and many other possibilities!
Interested to find out more? You can head to our product page for more!
Capacitive Proximity Sensors
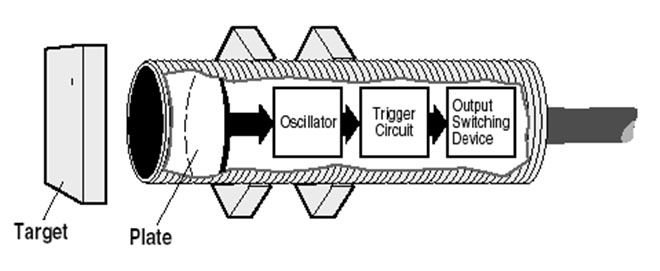
Capacitive proximity sensors are contactless sensors that detect both metallic and non-metallic objects, including liquid, powders, and granular. It operates by detecting a change in capacitance.
Similarly to inductive sensors, it consists of an oscillator, Schmitt trigger and output switching circuit. The only difference is it comprises of 2 charging plates (1 internal, 1 external) for capacitation:
- Internal plate connected to the oscillator
- External plate (sensor electrodes) used as the sensing surface
How do capacitive proximity sensors work?
- Capacitive proximity sensor produces an electrostatic field
- When an object (conductive/non-conductive) approaches the sensing area, the capacitance of both plates increases, resulting in oscillator amplitude gain
- The resulted amplitude gain triggers sensor output switch
*Note: Capacitive sensors only oscillate when the target object is present
Common applications:
- Industrial usages
- Production automation machines that count products, product transfers
- Filling processes, pipelines, inks, etc.
- Fluid level, composition, and pressure
- Moisture control
- Non-invasive content detection
- Touch applications
Advantages of Capacitive proximity sensors
- Contactless detection
- A wide array of materials able to be detected
- Able to detect objects through non-metallic walls with its wide sensitivity band
- Well-suited to be used in an industrial environment
- Contains potentiometer that allows users to adjust sensor sensitivity, such that only wanted objects will be sensed
- No moving parts, ensuring a longer service life
Disadvantages of Capacitive proximity sensors
- Relative low range, though incremental increase from inductive sensors
- Higher price as compared to inductive sensors
Grove – Capacitive Moisture Sensor (Corrosion Resistant)

Since we’ve now understood that capacitive proximity sensors are capable of moisture control, we’ll, of course, need a sensor for its applications!
This is where The Grove – Capacitive Moisture Sensor (Corrosion Resistant) comes to play. It’s a soil moisture sensor based on capacitance changes. Compared with resistive sensors, not only is it corrosion resistant, it offers a wide range of applications!
Interested to find out more? Head to our product page here!
Grove – 12 Key Capacitive I2C Touch Sensor V2 (MPR121)

Need a module that does more than just capacitative proximity sensing? We got just that!
The Grove – 12 Key Capacitive I2C Touch Sensor V2 (MPR121) is a 3-in-1 module with the following features: Capacitance Sensing, Touch Sensing, and Proximity Sensing.
To find out more information on it, you can head to our product page here!
Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors

Third on this list is ultrasonic proximity sensors, detecting the presence of objects through emitting high-frequency ultrasonic range. It does so through the conversion of electrical energy. Similarly to capacitive sensors, it can detect objects in solid, liquid, granular, or granular as well.
Probably the easiest among all, it only comprises an ultrasonic transmitter and an ultrasonic receiver.
How does Ultrasonic Proximity Sensor work?
- The sonic transducer emits sonic waves
- Sonic waves bounces off the object
- The wave that bounced off is then returned to the sensor
- Time that it took to emit and receive sound waves is then used to determine distance/proximity
Common applications
- Distance measurement
- Anemometers for wind speed and direction detection
- Automation production processes
- Fluid detection
- Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for object monitoring
- Robotics
Advantages of ultrasonic proximity sensors
- Contactless detection
- Not affected by object color and transparency
- Not affected by external environmental conditions, reliable solution
- Works well in places with extreme conditions
- Able to be used in dark environments
- Low current consumption
Disadvantages of an ultrasonic proximity sensors
- Limited detection range though capable of higher range as compared to inductive and capacitive sensors
- Doesn’t work in a vacuum since ultrasonic sensors operate via sound waves
- Not able to measure the distance of Soft objects or ones with extreme textures
Grove – Ultrasonic Sensor: Improved version of the HC-SR04

Made with significant benefits over the traditional HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, the Grove – Ultrasonic Sensor is the perfect ultrasonic module for not just proximity sensing, but as for distance measurement and ultrasonic detector. as well!
Interested to find out more? You can check out the following resources:
IR Proximity Sensor
IR, in short for infrared, detects the presence of an object by emitting a beam of infrared light. It works similarly to ultrasonic sensors, though instead of using sonic waves, IR is transmitted.
Infrared proximity sensors consist of an IR LED that emits, and a light detector for detection of reflection. It has an in-built signal processing circuit that determines an optical spot on the PSD.
How do IR proximity sensors work?
- Infrared light is emitted from the IR LED emitter
- The beam of light hits the object and gets reflected back in an angle
- The reflected light will reach the light detector
- The sensor in the light detector determines the position/distance of reflective object
Common applications
- Distance measurement
- Item counter; when object cuts the radiating light, it counts as one
- Security systems such as surveillance, burglar alarms, etc.
- Monitoring and control applications
Advantages of IR proximity sensors
- Contactless detection
- Applicable for daytime and nighttime usages
- Secured communication through a line of sight
- Able to measure the distance to soft objects unlike ultrasound proximity sensors
- Accuracy of the infrared sensor not affected by corrosion or oxidation
Disadvantages of IR proximity sensors
- Affected by environmental conditions and hard objects, implying inability fo usage through walls or doors
- Requires line of sight between transmitter and receiver for communication
- Performance dips over longer distances
Infrared Proximity Sensor offered at Seeed
Grove – 80cm Infrared Proximity Sensor

Based on the SHARP GP2Y0A21, this IR proximity sensor is a popular choice that I’m recommending for anyone that’s looking for accurate distance measuring beyond your alternatives.
Packed in a small package with low power consumption, this IR proximity sensor allows for continuous distance reading with a range of 10cm to 80cm!
Interested to find out more? You can check out the following resources:
How to choose a suitable proximity sensor
Now to help you select a suitable one out of the four, I’ve provided criteria that you should consider when making a proximity sensor selection.
However, as always, you’ll have to first consider your intended purpose; What are you trying to use it for in the first place.
| Proximity Sensor Crieria | How to select | Sensor Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Object requirements | Take a look at the object you’re planning to use a proximity sensor on Consider the following factors: Object color Shape of object Object material |
Most suited for complex object requirements: IR proximity sensor Not suited for complex object requirements: Ultrasonic proximity sensor |
| Environment of sensing | Take a look at the environment that you’re going to sense your object at Consider the following factors: Cleanliness Temperature Moisture |
Suited for harsh environment: Capacitive (most-suited) Inductive Ultrasonic Not suited for harsh environment: IR proximity sensor |
| Sensing Range/Distance | Take a look at whether your object will be placed close to the sensor face Consider the following factors: Distance between object placed and sensor (Far or Close) |
Suited for close range sensing: Inductive and Capacitive proximity sensors Suited for long range sensing: Ultrasonic and IR proximity sensors |
An additional factor that’s worth noting is the electrical system that you’re integrating the proximity sensor with. Be it, electrical load (NPN/PNP) or voltage supply (AC/DC), the sensor must function with the system controls you’re running.
Honorable mentions
Now that I’ve covered the criteria for proximity sensor consideration, here’s a list of some honorable mentions that are still worth taking a look at!
Photoelectric Proximity Sensor
Photoelectric proximity sensors are ones that use high-end photoelectric technology, it emits a light beam that’s capable of detecting all sorts of objects!
It has the following 3 different models; Reflective, Through-beam, and Retro-reflective. Each model offers varying light emission methods, though they are all highly efficient when it comes to distance detection.
If you’re interested in such proximity sensing technology, you can check this sensor that integrates it into a small package:
PSK-CM8JL65-CC5 Infrared Distance Measuring Sensor

Magnetic Proximity Sensor
Magnetic proximity sensors are proximity devices used to detect magnetic objects through their large sensing ranges. A typical one incorporates glass and metal blade, allowing for quick magnetizing!
Though it merely senses magnets, it’s still great for its low cost, long-range, and small dimensions.
If you fancy one and would like to know more about it, you can check out this:
Grove – 12-bit Magnetic Rotary Position Sensor / Encoder (AS5600)

Based on the A5600, this Magnetic Rotary Position Sensor is not only capable of contactless proximity sensing needs, but it contains significant advantages over regular encoders as well. Precise, programmable and cost-effective, it’s an option to consider!
Interested to find out more? You can head to our product page for more information!
LiDAR Proximity Sensor
LiDar, in short for Light Detection and Ranging, is a higher-end sensing technology that provides excellent max detection range with fast update rates. The only main downside is the cost, where it may be too costly for the average consumer.
Fear not though, here at Seeed, we offer a mini LiDAR proximity sensor that’s very much affordable!

Interested to find out more about it? You can head to our product page!
Summary
To summarise, here are the proximity sensors compared with its recommended usages:
For proximity sensor Arduino compatibility, You can consider the recommended Seeed products covered for each proximity sensor type! This will save you time in trying to make one yourself as well!
- Inductive sensor recommendation:
- Capacitive sensor recommendation:
- Ultrasonic sensor recommendation:
- IR sensor recommendation: