What is Mesh Network? Mesh Network vs WLAN
The traditional WLAN uses radio frequency technology to replace the old localized network of twisted copper wires with electromagnetic
What is Mesh Network?
However, wireless mesh networks are different and belong to multi-hop networks. Although also composed of a router and a client, several nodes constitute a backbone network and are connected to a wired internet network, which is responsible for providing a multi-hop wireless internet connection to the client. Wireless mesh networks remove the cabling requirements between nodes, but still have the redundancy and rerouting capabilities provided by distributed networks.
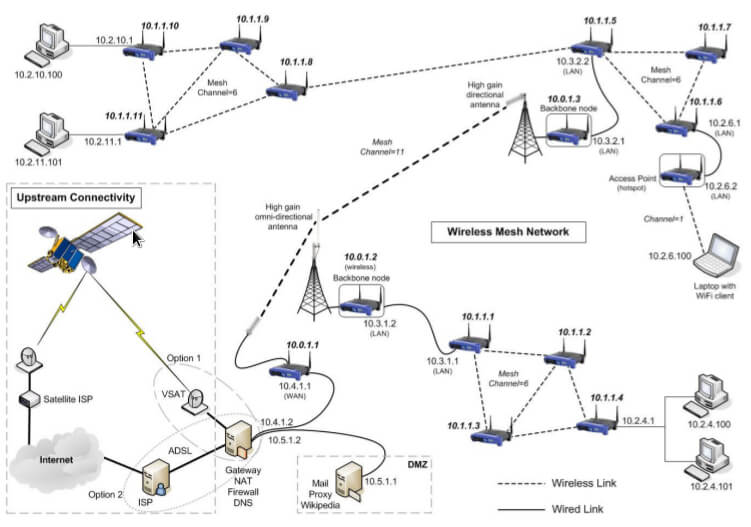
The biggest advantage of the mesh network and multi-hop access is that if the nearest AP is congested due to excessive traffic, the data can be automatically rerouted to a neighboring node with less traffic. The packet can also continue to be routed to the next node closest to it, depending on the network, until it reaches the final destination. Compared with the traditional switched network, the wireless mesh network removes the wiring requirements between
Here are a few advantages of wireless mesh networks:
- Cost-effective:
In wireless mesh networks, only MPP needs to access the wired network, and so the dependence on cabling is reduced to a minimum, eliminating the investment overhead of purchasing a large number of wired devices and installing them.
- Easy installation
The Mesh node is very simple. Just take the device out of the box and plug it in. By greatly simplifying installation, users can easily add new nodes to expand coverage and network capacity of the wireless network. In a wireless mesh network, not every mesh node requires a wired cable connection, which is the biggest difference from a wired AP.
- NLOS
NLOS configuration can be easily implemented using wireless mesh technology, so it has broad application prospects in outdoor and public places. A user with a direct line of sight with the transmitting station first receives the wireless signal and then forwards the received signal to another user without direct line of sight.
- Flexible and stable structure
In a single-hop network, devices must share APs. If several devices are to access the network at the same time, communication congestion may occur and the system may slow down. In a multi-hop network, devices can connect to the network through different nodes at the same time, so it does not cause system performance degradation. You don’t need to worry about data being delayed due to router failures.
- High bandwidth
Bandwidth is always an intractable problem. Because of the characteristics of wireless communication, bandwidth is easy to increase only when the transmission distance is short. However, the transmission distance of data is closely related to the signal strength, while the traditional single-center mode coverage area is limited. Due to the non-line-of-sight transmission characteristics of the wireless mesh network, the signal coverage is better and the strength is higher, and the total bandwidth can easily be improved. In addition, due to the role of the node relay, wireless mesh network signal coverage is excellent, so the power required for transmission is reduced, which is also helpful in saving energy. Therefore, choosing to transmit data through multiple short hops will be an effective way to obtain higher network bandwidth, a key advantage of m
Thanks to Particle Mesh, it is not
Mesh networking extends your networking to sense more data and stay connected where it counts
Refer to Particle’s instruction and tutorial by CNX Software you can find it is easy to set up you own mesh network and it is time to upgrading your router!
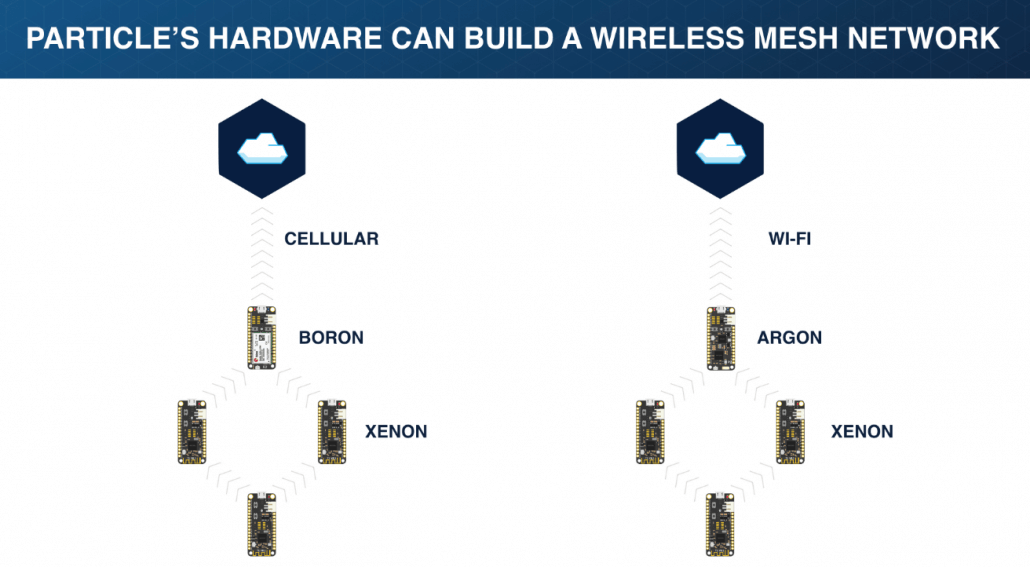
How does Particle Mesh work?
Particle Mesh is a wireless mesh network technology built on the Thread networking protocol, and designed to connect the spaces in between existing Wi-Fi and cellular deployments with local networks that are low-cost, secure, and ultra-reliable.
Building Particle Mesh with Openthread
Traditional IoT devices that use Wi-Fi and cellular connectivity rely on the cloud to transit between devices. However, Particle Mesh builds gateways to the Internet, and creates a local wireless grid that other devices can join. Particle Mesh provides a local network for every IoT device to understand and connect the world around it.
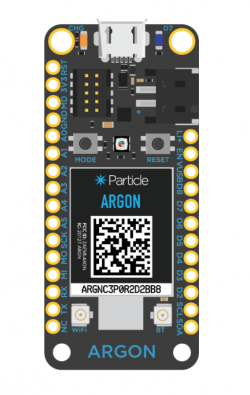
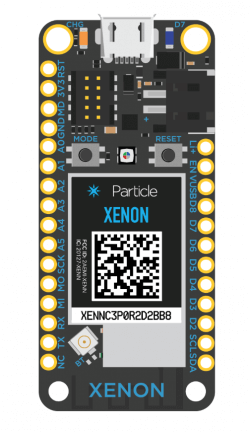
What are the differences between Particle Argon, Xenon and Boron?
The Particle Argon is a powerful Wi-Fi enabled development board that can act as either a standalone Wi-Fi endpoint or Wi-Fi enabled gateway for Particle Mesh networks. It is based on the Nordic nRF52840 and has built-in battery charging circuitry so it’s easy to connect a Li-Po and deploy your local network in minutes.
The Argon is great for connecting existing projects to the Particle Device Cloud or as a gateway to connect an entire group of local endpoints.
The Particle Boron LTE is a powerful LTE CAT-M1 enabled development kit that can act as either a standalone cellular endpoint or LTE enabled gateway for Particle Mesh networks. It is based on the Nordic nRF52840 and has built-in battery charging circuitry so it’s easy to connect a Li-Po and deploy your local network in minutes.
The Boron is great for connecting existing projects to the Particle Device Cloud or as a gateway to connect an entire group of local endpoints where Wi-Fi is missing or unreliable.
The Particle Xenon is a
The Xenon is mesh only and designed to function as the endpoint of your IoT network. It is based on the Nordic nRF52840 and has built-in battery charging circuitry so it’s easy to connect a Li-Po and deploy your local network in minutes.
The Xenon is best for connecting sensors, motors, pumps, valves, and points of data-interest. Pair it with an Argon or Boron gateway to get all that valuable data into the Particle Device Cloud.
It is not difficult to set up your own mesh network though nowadays hardware with full library and tutorials. Replace your router and try new mesh system with Particle Mesh now! Still have problems with Mesh? Let us know what’s on your mind!