Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Material Types and Comparison
The base material is an important part of printed circuit boards. It determines the PCB board’s performance and scope of application. Different products have different requirements for the PCB base material. With the development of electronic technology, the industry has to push the limits and overcome more and more challenges. None have been pushed to the extremes more than fiberglass copper clad laminates (CCL).
What are Copper Clad Laminates (CCL)?
Most PCB boards are made of copper clad laminates, otherwise referred to as cores. The core is what gives the boards structure and can influence other properties such as thermal resistance and impedance.The structure of CCL
Copper clad laminates consist of a sheet of fiberglass hardened with resin and copper foil laminated on one or both sides. The structure of the copper clad laminate can be divided into three layers: the substrate, copper foil and copper clad laminate adhesive: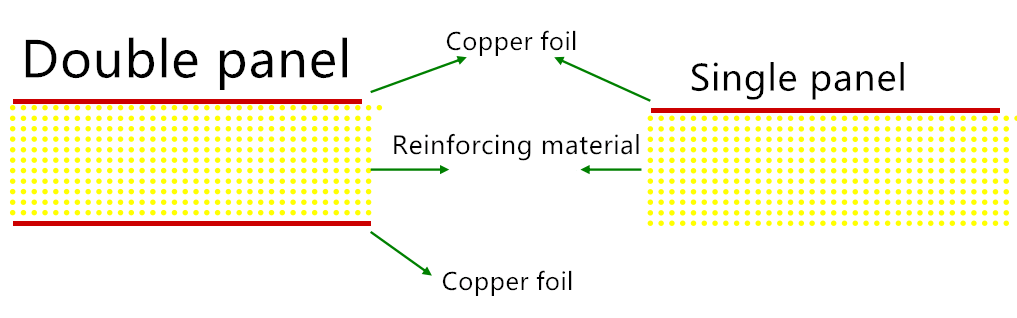
1. Substrate
The substrate for organic boards consists of an insulating material such as fiberglass or paper stacked together and impregnated with a synthetic resin. Many types of resins are used including phenolic resin, epoxy resin and polytetrafluroethylene.2. Copper foil
The copper foil plays an important part in circuit boards and in building the final copper thickness. The copper foil must have high conductivity and good weldability to help reduce the impedance of the circuit and facilitate welding of components. It is required that the surface of the copper foil shall not have scratches, blisters and wrinkles, the metal purity shall not be less than 99.8%, and the thickness error shall not exceed ±5um.3. Adhesive
The adhesive is key to maintaining a strong bond between the copper foil and substrate to prevent pads and traces from lifting during soldering and rough handling. The peel strength of the copper clad laminate is the measure of the adhesive’s strength.The role of CCL
CCL mainly plays the role of interconnection, insulation and support in the PCB, and has a great influence on the transmission speed, energy loss and characteristic impedance of the signal in the circuit. Therefore, CCL largely determines the performance, quality, processability, manufacturing level, manufacturing cost, and long-term reliability and stability of the PCB.Types of CCL: Rigid CCL and Flexible CCL
Generally speaking, CCL can be divided into two categories: Rigid Copper Clad Laminate and Flexible Copper Clad Laminate.Rigid Copper Clad Laminate can be divided into different types according to different factors such as insulating material, thickness, and reinforcing material. There are also many different types of Flexible Copper Clad Laminate.Rigid Copper Clad Laminate

Divided by insulating material and its structure
- Organic resin copper clad laminate
- Metal base (core) copper clad laminate
- Ceramic base copper clad laminate
Divided by the thickness of the CCL
- Conventional board
- Thin board
Divided by reinforced materials used by CCL
- Electronic glass fiber cloth base copper clad laminate
- Paper-based copper clad laminate
- Composite base copper clad laminate
Flexible Copper Clad Laminate
- Polyester film type (flame retardant and non-flame retardant)
- Polyimide film type (flame retardant, non-flame retardant, two-layer method and three-layer method)
- Ultra-thin electronic glass fiber cloth type
Flammability of CCL
Flammability is an important reference for evaluating PCB performance indicators. It is necessary to classify CCL based on flammability. According to flammability characteristics, we can divide PCB into UL-94 VO, UL-94 V1, UL-94 V2, UL-94 HB.UL-94 HB:
Normal cardboard (non- fireproof, the lowest grade material, cannot be made as power plate). The UL 94 standard is a test method standard for the combustion performance of materials developed by the American Underwriters Laboratory. “UL94 HB Class” is the lowest level of the classification of the combustion performance of materials in the UL94 standard.UL-94 V0:
flame retardant cardboard, 22F: single-sided fiber glass board CEM-1: single-sided fiber glass board CEM-3: double-sided half-glass board.High TG laminates
TG is the glass transition temperature, the temperature at which the material begins to soften and lose it’s rigidity. Another way of understanding the glass transition temperature is as the maximum temperature where the board is still rigid. It is lower than the melting point. A board with a higher TG can withstand higher operating temperatures without deforming or softening compared to a board with a lower TG rating.
Regular PCB material TG temperature is 130℃ to 135°C. High TG boards generally have a glass transition temperature greater than 170℃. Copper clad laminates with a TG temperature of 150°C are also common however, the higher the TG value, the more expensive the substrate. Higher TG materials are advantageous for boards to help withstand the higher temperatures required for lead-free assembly. Certain high level PCB manufacturing processes such as blind and buried vias, microvias also require greater heat resistance.Metal Clad Laminates
Aluminum boards use a different kind of core structure known as metal clad laminates (MCL) or metal cores (as in metal core PCB or MCPCB). The substrate consists of a metal, mainly aluminum which serves as the structural base and a heatsink as well. A thin layer of dielectric, typically FR4 prepreg with copper foil layer on top, is laminated on the other side. The prepreg serves to insulate the metal base from the circuitry. Most metal clad boards only have one copper layer, as increasing the layer count diminishes the heat conducting capabilities of the metal base. Double-sided aluminum boards are also very difficult to produce meaning the costs are much higher for lower performance. For those looking to have prototype or batch PCBs manufactured, and need a specialised laminate, check out Seeed Fusion instant online quoting platform for a wide range of material options and costs. Contact Seeed Studio Fusion for more information.